Innate immune sensing of cytosolic chromatin fragments through cGAS promotes senescence
- PMID: 28759028
- PMCID: PMC5826565
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3586
Innate immune sensing of cytosolic chromatin fragments through cGAS promotes senescence
Abstract
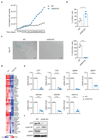
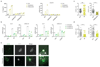
Cellular senescence is triggered by various distinct stresses and characterized by a permanent cell cycle arrest. Senescent cells secrete a variety of inflammatory factors, collectively referred to as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP). The mechanism(s) underlying the regulation of the SASP remains incompletely understood. Here we define a role for innate DNA sensing in the regulation of senescence and the SASP. We find that cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) recognizes cytosolic chromatin fragments in senescent cells. The activation of cGAS, in turn, triggers the production of SASP factors via stimulator of interferon genes (STING), thereby promoting paracrine senescence. We demonstrate that diverse stimuli of cellular senescence engage the cGAS-STING pathway in vitro and we show cGAS-dependent regulation of senescence following irradiation and oncogene activation in vivo. Our findings provide insights into the mechanisms underlying cellular senescence by establishing the cGAS-STING pathway as a crucial regulator of senescence and the SASP.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

