Low glycaemic index diets for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
- PMID: 28759107
- PMCID: PMC6483287
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004467.pub3
Low glycaemic index diets for the prevention of cardiovascular disease
Abstract
Background: The glycaemic index (GI) is a physiological measure of the ability of a carbohydrate to affect blood glucose. Interest is growing in this area for the clinical management of people at risk of, or with, established cardiovascular disease. There is a need to review the current evidence from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in this area. This is an update of the original review published in 2008.
Objectives: To assess the effect of the dietary GI on total mortality, cardiovascular events, and cardiovascular risk factors (blood lipids, blood pressure) in healthy people or people who have established cardiovascular disease or related risk factors, using all eligible randomised controlled trials.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase and CINAHL in July 2016. We also checked reference lists of relevant articles. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection criteria: We selected RCTs that assessed the effects of low GI diets compared to diets with a similar composition but a higher GI on cardiovascular disease and related risk factors. Minimum trial duration was 12 weeks. Participants included were healthy adults or those at increased risk of cardiovascular disease, or previously diagnosed with cardiovascular disease. Studies in people with diabetes mellitus were excluded.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently screened and selected studies. Two review authors independently assessed risk of bias, evaluated the overall quality of the evidence using GRADE, and extracted data following the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. We contacted trial authors for additional information. Analyses were checked by a second reviewer. Continuous outcomes were synthesized using mean differences and adverse events were synthesized narratively.
Main results: Twenty-one RCTs were included, with a total of 2538 participants randomised to low GI intervention (1288) or high GI (1250). All 21 included studies reported the effect of low GI diets on risk factors for cardiovascular disease, including blood lipids and blood pressure.Twenty RCTs (18 of which were newly included in this version of the review) included primary prevention populations (healthy individuals or those at high risk of CVD, with mean age range from 19 to 69 years) and one RCT was in those diagnosed with pre-existing CVD (a secondary prevention population, with mean age 26.9 years). Most of the studies did not have an intervention duration of longer than six months. Difference in GI intake between comparison groups varied widely from 0.6 to 42.None of the included studies reported the effect of low GI dietary intake on cardiovascular mortality and cardiovascular events such as fatal and nonfatal myocardial infarction, unstable angina, coronary artery bypass graft surgery, percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty, and stroke. The unclear risk of bias of most of the included studies makes overall interpretation of the data difficult. Only two of the included studies (38 participants) reported on adverse effects and did not observe any harms (low-quality evidence).
Authors' conclusions: There is currently no evidence available regarding the effect of low GI diets on cardiovascular disease events. Moreover, there is currently no convincing evidence that low GI diets have a clear beneficial effect on blood lipids or blood pressure parameters.
Conflict of interest statement
CC: None known.
LAK: None known.
EL: None known.
SAMK: None known.
LH: None known.
NF: None known.
RG: None known.
GF: None of the relationships described are felt to be a conflict of interest regarding this publication. Consultancy for appetite regulation with Unilever; grant application to Nestle on modified cereal fibre and glycaemic control (awaiting outcome); patent on compounds and their effects on appetite control and insulin sensitivity (WO2014020344 A1).
KR: None known.
Figures
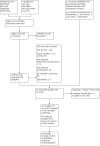




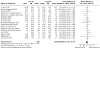



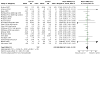
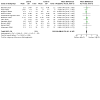


Update of
-
Low glycaemic index diets for coronary heart disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD004467. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004467.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 31;7:CD004467. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004467.pub3. PMID: 15495112 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Armendariz‐Anguiano 2011 {published data only}
-
- Armendariz-Anguiano AL, Jimenez-Cruz A, Bacardi-Gascon M, Hurtado-Ayala L. Effect of a low glycemic load on body composition and Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) in overweight and obese subjects. Nutricion Hospitalaria 2011;26:170-5. - PubMed
Bellisle 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bellisle F, Dalix AM, De Assis MA, Kupek E, Gerwig U, Slama G, et al. Motivational effects of 12-week moderately restrictive diets with or without special attention to the glycaemic Index of foods. British Journal of Nutrition 2007;97:790-8. - PubMed
Buscemi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Buscemi S, Cosentino L, Rosafio G, Morgana M, Mattina A, Sprini D, et al. Effects of hypocaloric diets with different glycemic indexes on endothelial function and glycemic variability in overweight and in obese adult patients at increased cardiovascular risk. Clinical Nutrition 2013;32:346-52. - PubMed
DiOGenes 2011a high protein {published data only}
-
- Aller EE, Larsen TM, Claus H, Lindroos AK, Kafatos A, Pfeiffer A, et al. Weight loss maintenance in overweight subjects on ad libitum diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index: the DIOGENES trial 12-month results. International Journal of Obesity 2014;28(12):1511-7. - PubMed
-
- Gogebakan O, Kohl A, Osterhoff MA, Van Baak MA, Jebb SA, Papadaki A, et al. Effects of weight loss and long-term weight maintenance with diets varying in protein and glycemic index on cardiovascular risk factors: the diet, obesity, and genes (DiOGenes) study: a randomized, controlled trial. Circulation 2011;124:2829-38. - PubMed
-
- Goyenechea E, Holst C, Van Baak M, Saris W, Jebb S, Kafatos A, et al. Effects of different protein content and glycaemic index of ad libitum diets on diabetes risk factors in overweight adults: the DIOGenes multicentre, randomized, dietary intervention trial. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2011;27(7):705-16. - PubMed
-
- Larsen T M, Dalskov S, Baak M, Jebb S, Kafatos A, Pfeiffer A, et al. The Diet, Obesity and Genes (Diogenes) Dietary Study in eight European countries - a comprehensive design for long-term intervention. Obesity Reviews 2010;11:76-91. - PubMed
DiOGenes 2011 low protein {published data only}
-
- Aller EE, Larsen TM, Claus H, Lindroos AK, Kafatos A, Pfeiffer A, et al. Weight loss maintenance in overweight subjects on ad libitum diets with high or low protein content and glycemic index: the DIOGENES trial 12-month results. International Journal of Obesity 2014;28(12):1511-7. - PubMed
-
- Gogebakan O, Kohl A, Osterhoff MA, Van Baak MA, Jebb SA, Papadaki A, et al. Effects of weight loss and long-term weight maintenance with diets varying in protein and glycemic index on cardiovascular risk factors: the diet, obesity, and genes (DiOGenes) study: a randomized, controlled trial. Circulation 2011;124:2829-38. - PubMed
-
- Goyenechea E, Holst C, Van Baak M, Saris W, Jebb S, Kafatos A, et al. Effects of different protein content and glycaemic index of ad libitum diets on diabetes risk factors in overweight adults: the DIOGenes multicentre, randomized, dietary intervention trial. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 2011;27(7):705-16. - PubMed
-
- Larsen T M, Dalskov S, Baak M, Jebb S, Kafatos A, Pfeiffer A, et al. The Diet, Obesity and Genes (Diogenes) Dietary Study in eight European countries - a comprehensive design for long-term intervention. Obesity Reviews 2010;11:76-91. - PubMed
Frost 2004 {published data only}
-
- Frost GS, Brynes AE, Bovill-Taylor C, Dornhorst A. A prospective randomised trial to determine the efficacy of a low glycaemic index diet given in addition to healthy eating and weight loss advice in patients with coronary heart disease. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004;58:121-7. - PubMed
Ghani 2014a high insulin {published data only}
-
- Fatimah A, Rohana AG, Norasyikin AW, Karuthan C, Nik Shanita S, Mohd Yusof BN, et al. Lowering dietary glycaemic index through nutrition education among Malaysian women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition 2013;19(1):9-23. - PubMed
-
- Shyam S, Arshad F, Abdul Ghani R, Abdul Wahab N, Barakatun Nisak M, Safii N, et al. Women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus achieve clinically significant weight loss on low glycaemic index diets. In: Obesity Reviews. Vol. 15. 2014:92.
Ghani 2014 low insulin {published data only}
-
- Fatimah A, Rohana AG, Norasyikin AW, Karuthan C, Nik Shanita S, Mohd Yusof BN, et al. Lowering dietary glycaemic index through nutrition education among Malaysian women with a history of gestational diabetes mellitus. Malaysian Journal of Nutrition 2013;19(1):9-23. - PubMed
-
- Shyam S, Arshad F, Abdul Ghani R, Abdul Wahab N, Barakatun Nisak M, Safii N, et al. Women with previous gestational diabetes mellitus achieve clinically significant weight loss on low glycaemic index diets. In: Obesity Reviews. Vol. 15. 2014:92.
Hönemann 2010 {published data only}
-
- Hönemann I, Ranke C, Austel A, Jarzemski S, Deeken I, Pleyer I, et al. Changes of cardiovascular risk factors while following one of three currently discussed dietetic weight-reducing strategies [Veränderungen kardiovaskulärer Risikofaktoren unter drei aktuell diskutierten Ernährungsstrategien zur Gewichtsreduktion]. Aktuelle Ernahrungsmedizin 2010;35:227-35.
Juanola‐Falgarona 2014 {published data only}
-
- Giardina S, Hernandez Alonso P, Salas Salvado J, Bullo M. Effects of Glycemic index on the expression of selected miRNAs in adipose tissue: the GLYNDIET study. In: Obesity facts. Vol. 9. 2016:223.
-
- Juanola-Falgarona M, Ibarrola N, Salvadó JS, Soler AR, Bulló M. Design and methods of the GLYNDIET study; assessing the role of glycemic index on weight loss and metabolic risk markers. Nutrición Hospitalaria 2013;28(2):382-90. - PubMed
-
- Juanola-Falgarona M, Salas-Salvadó J, Ibarrola-Jurado N, Rabassa-Soler A, Bulló M. Effect of dietary glycemic index and glycemic load on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors: the GLYNDIET Study. In: Obesity Facts. Vol. 6. 2013:111.
-
- Juanola-Falgarona M, Salas-Salvadó J, Ibarrola-Jurado N, Rabassa-Soler A, Díaz-López A, Guasch-Ferré M, et al. Effect of the glycemic index of the diet on weight loss, modulation of satiety, inflammation, and other metabolic risk factors: a randomized controlled trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014;11(1):27-35. - PubMed
McMillan‐Price 2006 high CHO {published data only}
-
- McMillan-Price J, Petocz P, Atkinson F, O'Neill K, Samman S, Steinbeck K, et al. Comparison of 4 diets of varying glycemic load on weight loss and cardiovascular risk reduction in overweight and obese young adults: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166:1466-75. - PubMed
McMillan‐Price 2006 high protein {published data only}
-
- McMillan-Price J, Petocz P, Atkinson F, O'Neill K, Samman S, Steinbeck K, et al. Comparison of 4 diets of varying glycemic load on weight loss and cardiovascular risk reduction in overweight and obese young adults: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Internal Medicine 2006;166:1466-75. - PubMed
Melanson 2012 {published data only}
-
- Melanson KJ, Summers A, Nguyen V, Brosnahan J, Lowndes J, Angelopoulos TJ, et al. Body composition, dietary composition, and components of metabolic syndrome in overweight and obese adults after a 12-week trial on dietary treatments focused on portion control, energy density, or glycemic index. Nutrition Journal 2012;11:57. - PMC - PubMed
Philippou 2008 {published data only}
-
- Philippou E, McGowan BM, Brynes AE, Dornhorst A, Leeds AR, Frost GS. The effect of a 12-week low glycaemic index diet on heart disease risk factors and 24 h glycaemic response in healthy middle-aged volunteers at risk of heart disease: a pilot study. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;62:145-9. - PubMed
Philippou 2009 {published data only}
-
- Philippou E, Bovill-Taylor C, Rajkumar C, Vampa ML, Ntatsaki E, Brynes AE, et al. Preliminary report: the effect of a 6-month dietary glycemic index manipulation in addition to healthy eating advice and weight loss on arterial compliance and 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure in men: a pilot study. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental 2009;58:1703-8. - PubMed
Philippou 2009a {published data only}
-
- Philippou E, Neary NM, Chaudhri O, Brynes AE, Dornhorst A, Leeds AR, et al. The effect of dietary glycemic index on weight maintenance in overweight subjects: a pilot study. Obesity 2009;17:396-401. - PubMed
Raatz 2005 {published data only}
-
- Raatz SK, Torkelson CJ, Redmon JB, Reck KP, Kwong CA, Swanson JE, et al. Reduced glycemic index and glycemic load diets do not increase the effects of energy restriction on weight loss and insulin sensitivity in obese men and women. Journal of Nutrition 2005;135:2387-91. - PubMed
Randolph 2014 {published data only}
-
- NCT01186393. Effects of potatoes in a weight loss program (BBFUSPB). clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01186393?term=NCT01186393&rank=1 (accessed on June 2016).
-
- Randolph J, Edirisinghe I, Kappagoda CT, Burton-Freeman B. Glycemic index and potato consumption: effects on glucose metabolism and body composition. In: Obesity. Vol. 18. 2010:S91.
-
- Randolph JM, Edirisinghe I, Masoni AM, Kappagoda T, Burton-Freeman B. Potatoes, glycemic index, and weight loss in free-living individuals: practical implications. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2014;33(5):375-84. - PubMed
RISCK 2010 high MUFA {published data only}
-
- Jebb SA, Lovegrove JA, Griffin BA, Frost GS, Moore CS, Chatfield MD, et al. Effect of changing the amount and type of fat and carbohydrate on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk: the RISCK (Reading, Imperial, Surrey, Cambridge, and Kings) trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92:748-58. - PMC - PubMed
RISCK 2010 low fat {published data only}
-
- Jebb SA, Lovegrove JA, Griffin BA, Frost GS, Moore CS, Chatfield MD, et al. Effect of changing the amount and type of fat and carbohydrate on insulin sensitivity and cardiovascular risk: the RISCK (Reading, Imperial, Surrey, Cambridge, and Kings) trial. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92:748-58. - PMC - PubMed
Shikany 2005 {published data only}
-
- Shikany JM, Goudie A, Oberman A. Comparison of a low-fat/low-glycemic index diet to a low-fat only diet in the treatment of adults with hypercholesterolemia. Nutrition Research 2005;25:971-81.
Sichieri 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sichieri R, Moura AS, Genelhu V, Hu F, Willett WC. An 18-mo randomized trial of a low-glycemic-index diet and weight change in Brazilian women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;86:707-13. - PubMed
Solomon 2010 {published data only}
-
- Solomon TP, Haus JM, Kelly KR, Cook MD, Filion J, Rocco M, et al. A low-glycemic index diet combined with exercise reduces insulin resistance, postprandial hyperinsulinemia, and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide responses in obese, prediabetic humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92:1359-68. - PMC - PubMed
Venn 2010 {published data only}
-
- Venn BJ, Perry T, Green TJ, Skeaff CM, Aitken W, Moore NJ, et al. The effect of increasing consumption of pulses and wholegrains in obese people: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2010;29:365-72. - PubMed
Wolever 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Wolever TMS, Mehling C. High carbohydrate-low glycaemic index dietary advice improves glucose disposition index in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. British Journal of Nutrition 2002;87:477-87. - PubMed
-
- Wolever TMS, Mehling C. Long-term effect of varying the source or amount of dietary carbohydrate on postprandial plasma glucose, insulin, triacylglycerol and free fatty acid concentrations in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003;77(3):612-21. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Abbasi 2000 {published data only}
-
- Abbasi F, McLaughlin T, Lamendola C, Kim HS, Tanaka A, Wang T, et al. High carbohydrate diets, triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, and coronary heart disease risk. American Journal of Cardiology 2000;85:45-8. - PubMed
Abete 2008 {published data only}
-
- Abete I, Parra D, Martinez JA. Energy-restricted diets based on a distinct food selection affecting the glycemic index induce different weight loss and oxidative response. Clinical Nutrition 2008;27:545-51. - PubMed
Agus 2000 {published data only}
Alfenas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Alfenas RCG, Mattes RD. Influence of glycemic index/load on glycemic response, appetite, and food intake in healthy humans. Diabetes Care 2005;28(9):2123-9. - PubMed
Alfenas 2012 {published data only}
-
- Alfenas RCG. The consumption of low glycemic meals reduces abdominal obesity in subjects with excess body weight. Nutricion Hospitalaria 2012;27:1178-83. - PubMed
Amano 2007 {published data only}
-
- Amano Y, Sugiyama M, Lee JS, Kawakubo K, Mori K, Tang AC, et al. Glycemic index-based nutritional education improves blood glucose control in Japanese adults: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1874-6. - PubMed
Argiana 2011 {published data only}
-
- Argiana V, Kanellos P, Elefteriadou I, Alexiadou K, Grigoropoulou P, Tsitsinakis G, et al. The role of glycaemic index and glycaemic load on weight loss and on the metabolic parameters of adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2011;54:S354.
Aston 2008 {published data only}
Bahadori 2005 {published data only}
-
- Bahadori B, Yazdani-Biuki B, Krippl P, Brath H, Uitz E, Wascher TC. Low-fat, high carbohydrate (low glycaemic index) diet induces weight loss and preserves lean body mass in obese healthy subjects: results of a 24 week study. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2005;7:290-3. - PubMed
Barakatun 2010 {published data only}
-
- Barakatun Nisak MY, Ruzita AT, Norimah AK, Gilbertson H, Nor Azmi K. Improvement of dietary quality with the aid of a low glycemic index diet in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2010;29:161-70. - PubMed
Barkoukis 2002 {published data only}
-
- Barkoukis H, Fiedler KM, Lerner E. A combined high-fiber, low-glycemic index diet normalizes glucose tolerance and reduces hyperglycemia and hyperinsulinemia in adults with hepatic cirrhosis. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2002;102:1503-7. - PubMed
Bouche 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bouche C, Rizkalla SW, Luo J, Vidal H, Veronese A, Pacher N, et al. Five-week, low glycemic index diet decreases total fat mass and improves plasma lipid profile in moderately overweight nondiabetic men. Diabetes Care 2002;25(5):822-8. - PubMed
Brand 1991 {published data only}
-
- Brand JC, Colagiuri S, Crossman S, Allen A, Roberts DCK, Truswell AS. Low-glycemic index foods improve long-term glycemic control in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1991;14(2):95-101. - PubMed
Brynes 2003 {published data only}
-
- Brynes AE, Edwards CM, Ghatei MA, Dornhorst A, Morgan LM, Bloom SR, et al. A randomised four-intervention crossover study investigating the effect of carbohydrates on daytime profiles of insulin, glucose, non-esterified fatty acids and triacylglycerols in middle-aged men. British Journal of Nutrition 2003;89:207-18. - PubMed
Calle‐Pascual 1988 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Calle-Pascual AL, Gomez V, Leon E, Bordiu E. Foods with a low glycemic index do not improve glycemic control of both type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients after one month of therapy. Diabete et Metabolisme 1988;14(5):629-33. - PubMed
Carels 2005 {published data only}
-
- Carels RA, Darby LA, Douglass OM, Cacciapaglia HM, Rydin S. Education on the glycemic index of foods fails to improve treatment outcomes in a behavioral weight loss program. Eating Behaviours 2005;5:145-50. - PubMed
Chanteleau 1985 {published data only}
-
- Chanteleau E, Sonnenburg GE, Kunze K, Berger M. Importance of the glycaemic index of carbohydrate-containing foods for metabolic control of type 1 diabetics under insulin pump therapy [Die Bedeutung des glykämischen Index kohlenhydrathaltiger Lebensmittel für die Stoffwechselkontrolle von Typ1 Diabetikern unter Insulinpumpentherapie]. Aktuelle Ernährungsmedizin Klinik und Praxis 1985;10:236-40.
Cheong 2009 {published data only}
-
- Cheong SH, McCargar LJ, Paty BW, Tudor-Locke C, Bell RC. The First Step First Bite Program: guidance to increase physical activity and daily intake of low-glycemic index foods. Journal of the American Dietetic Association 2009;109:1411-6. - PubMed
Chiavaroli 2016 {published data only}
-
- Chiavaroli L, Mirrahimi A, Ireland C, Mitchell S, Sahye-Pudaruth S, Coveney J, Olowoyeye O, Maraj T, Patel D, Souza RJ, Augustin LS. Low-glycaemic index diet to improve glycaemic control and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: design and methods for a randomised, controlled, clinical trial. BMJ open 2016;6(7):e012220. - PMC - PubMed
Clapp 1998 {published data only}
-
- Clapp JF. Effect of dietary carbohydrate on the glucose and insulin response to mixed caloric intake and exercise in both nonpregnant and pregnant women. Diabetes Care 1998;21:106-13. - PubMed
Colagiuri 1986 {published data only}
-
- Colagiuri S, Miller JJ, Holliday JL, Phelan E. Comparison of plasma glucose, serum Insulin, and C-peptide responses to three isocaloric breakfasts in non-insulin-dependant diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 1986;9:250-5. - PubMed
Collier 1986 {published data only}
-
- Collier GR, Wolever TMS, Wong GS, Josse RG. Prediction of glycemic response to mixed meals in noninsulin-dependant diabetic subjects. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1986;44:349-52. - PubMed
Collier 1988 {published data only}
-
- Collier GR, Giudici S, Kalmusky J, Wolever TMS, Helman G, Wesson V, et al. Low glycaemic index starchy foods improve glucose control and lower serum cholesterol in diabetic children. Diabetes, Nutrition and Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental 1988;1:11-9.
Coulston 1984 {published data only}
-
- Coulston AM, Hollenbeck CB, Liu GC, Williams RA, Starich GH, Mazzaferri EL, et al. Effect of source of dietary carbohydrate on plasma glucose, insulin, and gastric inhibitory polypeptide responses to test meals in subjects with noninsulin-dependant diabetes mellitus. American Society of Clinical Nutrition 1984;40:965-70. - PubMed
Crapo 1981 {published data only}
-
- Crapo PA, Insel J, Sperling M, Kolterman OG. Comparison of serum glucose, insulin, and glucagon responses to different types of complex carbohydrate in noninsulin-dependant diabetic patients. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1981;34:184-90. - PubMed
De Rougemont 2007 {published data only}
-
- De Rougemont A, Normand S, Nazare JA, Skilton MR, Sothier M, Vinoy S, et al. Beneficial effects of a 5-week low-glycaemic index regimen on weight control and cardiovascular risk factors in overweight non-diabetic subjects. British Journal of Nutrition 2007;98:1288-98. - PubMed
Dumesnil 2001 {published data only}
-
- Dumesnil JG, Turgeon J, Tremblay A, Poirer P, Gilbert M, Gagnon L, et al. Effect of a low-glycaemic Index-low-fat-high protein diet on the atherogenic metabolic risk profile of abdominally obese men. British Journal of Nutrition 2001;86:557-68. - PubMed
Ebbeling 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ebbeling CB, Leidig MM, Sinclair KB, Hangen JP, Ludwig DS. A reduced glycemic load diet in the treatment of adolescent obesity. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2003;157:773-9. - PubMed
Ebbeling 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ebbeling CB, Leidig MM, Sinclair KB, Seger-Shippee LG, Feldman HA, Ludwig DS. Effects of an ad libitum low glycemic load diet on cardiovascular disease risk factors in obese young adults. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005;81:976-82. - PubMed
Fontvielle 1988 {published data only}
-
- Fontvieille AM, Acosta M, Rizkalla SW, Bornet F, David P, Letanoux M, et al. A moderate switch from high to low glycaemic-index foods for 3 weeks improves the metabolic control of Type I (IDDM) diabetic subjects. Diabetes, Nutrition and Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental 1988;1:139-43.
Fontvielle 1992 {published data only}
-
- Fontvielle AM, Rizkalla SW, Penfornis A, Acosta M, Bornet FRJ, Slama G. The use of low glycaemic index foods improves metabolic control of diabetic patients over five weeks. Diabetic Medicine 1992;9:444-50. - PubMed
Frost 1994 {published data only}
-
- Frost G, Wilding J, Beecham J. Dietary advice based on the glycaemic index improves dietary profile and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetic Medicine 1994;11:397-401. - PubMed
Frost 1996 {published data only}
-
- Frost G, Keogh B, Smith D, Akinsanya K, Leeds A. The effect of low-glycemic carbohydrate on insulin and glucose response in vivo and in vitro in patients with coronary heart disease. Metabolism 1996;45(6):669-72. - PubMed
Frost 1998a {published data only}
-
- Frost G, Leeds A, Trew G, Margara R, Dornhurst A. Insulin sensitivity in women at risk of coronary heart disease and the effect of a low glycemic diet. Metabolism 1998;47(10):1245-51. - PubMed
Frost 1998b {published data only}
-
- Frost GE, Keogh BE, Smith D, Leeds AR, Dornhorst A. Reduced adipocyte insulin sensitivity in Caucasian and Asian subjects with coronary heart disease. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15:1003-9. - PubMed
Frost 1999 {published data only}
-
- Frost G, Leeds AA, Dore CJ, Madeiros S, Brading S, Dornhurst A. Glycaemic index as a determinant of serum HDL-cholesterol concentration. Lancet 1999;353:1045-8. - PubMed
Fuh 1990 {published data only}
-
- Fuh MMT, Lee MMS, Jeng CY, Ma F, Chen I, Reavem GM. Effect of low fat-high carbohydrate diets in hypertensive patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Hypertension 1990;3:527-32. - PubMed
Garg 1988 {published data only}
-
- Garg A, Bonanome A, Grundy SM, Zhang ZU, Unger RH. Comparison of a high-carbohydrate diet with a high-monounsaturated-fat diet in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New England Journal of Medicine 1988;13:828-35. - PubMed
Garg 1992 {published data only}
-
- Garg A, Grundy SM, Unger RH. Comparison of effects of high and low carbohydrate diets on plasma lipoproteins and insulin sensitivity in patients with mild NIDDM. Diabetes 1992;41:1278-85. - PubMed
Garg 1994 {published data only}
-
- Garg A, Bantle JP, Henry RR, Coulston AM, Griver KA, Raatz SK, et al. Effects of varying carbohydrate content of diet in patients with non-insulin-dependant diabetes mellitus. JAMA 1994;271:1420-9. - PubMed
Giacco 2000 {published data only}
-
- Giacco R, Parillo M, Rivellese AA, Lasorella G, Giacco A, D'Episcopo L, et al. Long-term dietary treatment with increased amounts of fiber-rich low-glycemic index natural foods improves blood glucose control and reduces the number of hypoglycemic events in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2000;23(10):1461-6. - PubMed
Gilbertson 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gilbertson HR, Brand-Miller JC, Thornburn AW, Evans S, Chondros P, Werther GA. The effect of flexible low glycemic index dietary advice versus measured carbohydrate exchange diets on glycemic control in children with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2001;24(7):1137-43. - PubMed
Gilbertson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gilbertson HR, Thornburn AW, Brand-Miller JC, Chondros P, Werther GA. Effect of low glycaemic-index dietary advice on dietary quality and food choice in children with type 1 diabetes. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003;77:83-90. - PubMed
Golay 1992 {published data only}
-
- Golay A, Koellreutter B, Bloise D, Assal JP, Wursch P. The effect of muesli or cornflakes at breakfast on carbohydrate metabolism in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 1992;15:135-42. - PubMed
Grant 2010 {published data only}
-
- Grant S, Wolever TMS, O'Connor DL, Josse RG. The effect of a low glycemic index diet on gestational hyperglycemia: a pilot trial. Federation of the American Societies of Experimental Biology Journal 2010;19(11):15-22.
Gutschall 2009 {published data only}
-
- Gutschall MD, Miller CK, Mitchell DC, Lawrence FR. A randomized behavioural trial targeting glycaemic index improves dietary, weight and metabolic outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. Public Health Nutrition 2009;12:1846-54. - PubMed
Heilbronn 2002 {published data only}
-
- Heilbronn LK, Noakes M, Clifton PM. The effect of high- and low-glycemic index energy restricted diets on plasma lipid and glucose profiles in type 2 diabetic subjects with varying glycemic control. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2002;21(2):120-7. - PubMed
Herrmann 2001 {published data only}
-
- Herrmann TS, Bean ML, Black TM, Wang P, Coleman RA. High glycemic index carbohydrate diet alters the diurnal rhythm of leptin but not insulin concentrations. Experimental Biology & Medicine 2001;226:1037-44. - PubMed
Hollenbeck 1985 {published data only}
-
- Hollenbeck CB, Riddle MC, Connor WE, Leklem JE. The effects of subject-selected high carbohydrate, low fat diets on glycemic control in insulin dependant diabetes mellitus. American Society for Clinical Nutrition 1985;41:293-8. - PubMed
Jarvi 1995 {published data only}
-
- Jarvi AE, Karlstrom BE, Granfeldt YE, Bjorck IME, Vessby BOH, Asp LN. The influence of food structure on postprandial metabolism in patients with non-insulin-dependant diabetes mellitus. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;61:837-43. - PubMed
Jarvi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Jarvi A, Karlstrom B, Granfeldt Y, Bjorck I, Asp NG, Vessby B. Improved glycemic control and lipid profile and normalized fibrinolytic activity on a low glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 1999;22:10-8. - PubMed
Jenkins 1985 {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJA, Wolever TMS, Kalmusky J, Giudici S, Giordano C, Wong GS, et al. Low glycemic index carbohydrate foods in the management of hyperlipidemia. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1985;42:604-17. - PubMed
Jenkins 1987a {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJA, Wolever TMS, Collier GR, Ocana A, Rao AV, Buckley G, et al. Metabolic effects of a low-glycemic-index diet. American Society for Clinical Nutrition 1987;46:968-75. - PubMed
Jenkins 1987b {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJA, Wolever TMS, Kalmusky J, Guidici S, Giordano C, Patten R, et al. Low glycemic index diet in hyperlipidemia: use of traditional starchy foods. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1987;46:66-71. - PubMed
Jenkins 1988 {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJA, Wolever TMS, Buckley G, Lam KY, Giudici S, Kalmusky J, et al. Low glycemic index starchy foods in the diabetic diet. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1988;48:248-54. - PubMed
Jenkins 2002a {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJA, Kendall CWC, Augustin LSA, Martini MC, Axelsen M, Faulkner D, et al. Effect of wheat bran on glycemic control and risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002;25:1522-8. - PubMed
Jenkins 2002b {published data only}
-
- Jenkins AL, Jenkins DJA, Zdravkovic U, Wursch P, Vuksan V. Depression of the glycemic index by high levels of B-glucan fiber in two functional foods tested in type 2 diabetes. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;56:622-8. - PubMed
Jenkins 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jenkins DJ, Kendall CW, McKeown-Eyssen G, Josse RG, Silverberg J, Booth GL, et al. Effect of a low-glycemic index or a high-cereal fiber diet on type 2 diabetes: a randomized trial. JAMA 2008;300:2742-53. - PubMed
Jensen 2008 {published data only}
-
- Jensen L, Sloth B, Krog-Mikkelsen I, Flint A, Raben A, Tholstrup T, et al. A low-glycemic-index diet reduces plasma plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 activity, but not tissue inhibitor of proteinases-1 or plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 protein, in overweight women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008;87:97-105. - PubMed
Jeppesen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Jeppensen J, Schaaf P, Jones C, Zhou MY, Chen IYD, Reaven GM. Effects of low-fat, high-carbohydrate diets on risk factors for ischemic heart disease in postmenopausal women. American Society for Clinical Nutrition 1997;65:1027-33. - PubMed
Jimenez‐Cruz 2003a {published data only}
-
- Jimenez-Cruz A, Bacardi-Gascon M, Turnbull WH, Rosales G, Severino-Lugo I. A flexible, low-glycemic index Mexican-style diet in overweight and obese subjects with type 2 diabetes improves metabolic parameters during a 6-week treatment period. Diabetes Care 2003;26(7):1967-70. - PubMed
Jiminez‐Cruz 2003b {published data only}
-
- Jiminez-Cruz A, Seimandi-Mora H, Bacardi-Gascon M. Effect of low glycemic index diet in hyperlipidemia [Efecto de dietas con bajo indice glucemico en hiperlipidemicos]. Nutricion Hospitalaria 2003;18(6):331-5. - PubMed
Jiminez‐Cruz 2004 {published data only}
-
- Jiminez-Cruz A, Turnbull WH, Bacardi-Gascon MB, Rosales-Garay P. A high fiber, moderate-glycemic index, Mexican style diet improves dyslipidemia in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Nutrition Research 2004;24(1):19-27.
Kabir 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kabir M, Oppert J-M, Vidal H, Bruzzo F, Fiquet C, Wursch P, et al. Four-week low-glycemic index breakfast with a modest amount of soluble fibers in type 2 diabetic men. Metabolism 2002;51(7):819-26. - PubMed
-
- Kabir M, Rizkalla SW, Oppert J-M, Wursch P, Bruzzo F, Slama G. Chronic effects of a low glycemic index starch breakfast on glucose and lipid metabolism in type 2 diabetic men: results of a controlled study. Diabetes 1999;48(Suppl 1):A461.
Kelly 2011 {published data only}
Kendall 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kendall CWC, Augustin LS, Mitchell S, Sahye-Pudaruth S, Coveney J, Cerovic A, et al. Effect of pulses as part of a low glycemic index diet compared to a high fiber diet on HbA1c and blood lipids in type 2 diabetes. Federation of the American Societies of Experimental Biology Journal 2012;26:5.
Kiens 1996 {published data only}
-
- Kiens B, Richter EA. Types of carbohydrate in an ordinary diet affect insulin action and muscle substrates in humans. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1996;63:47-53. - PubMed
Komindr 2001 {published data only}
-
- Komindr S, Ingsriswang S, Lerdvuthisopon N, Boontawee A. Effect of long-term intake of Asian food with different glycaemic indices on diabetic control and protein conservation in type 2 diabetic patients. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand 2001;84(1):85-97. - PubMed
Krog‐Mikkelsen 2011 {published data only}
-
- Krog-Mikkelsen I, Sloth B, Dimitrov D, Tetens I, Bjorck I, Flint A, et al. A low glycemic index diet does not affect postprandial energy metabolism but decreases postprandial insulinemia and increases fullness ratings in healthy women. Journal of Nutrition 2011;141:1679-84. - PubMed
Kwak 2012 {published data only}
-
- Kwak JH, Paik JK, Kim HI, Kim OY, Shin DY, Kim HJ, et al. Dietary treatment with rice containing resistant starch improves markers of endothelial function with reduction of postprandial blood glucose and oxidative stress in patients with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2012;224:457-64. - PubMed
Lafrance 1998 {published data only}
-
- Lafrance L, Rabasa-Lhoret R, Poisson D, Ducros F, Chiasson J-L. The effects of different glycaemic index foods and dietary fibre intake on glycaemic control in type 1 diabetic patients on intensive insulin therapy. Diabetic Medicine 1998;15:972-8. - PubMed
LaHaye 2005 {published data only}
-
- LaHaye SA, Hollett PM, Vyselaar JR, Shakchi M, Lahey KA, Day AG. Comparison between a low glycemic load diet and a Canada Food Guide diet in cardiac rehabilitation patients in Ontario. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2005;21(6):489-94. - PubMed
Laitinen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Laitinen JH, Ahola IE, Sarkkinen ES, Winberg RL, Harmaakorpi-IIvonen PA, Uusitupa MI. Impact of intensified dietary therapy on energy and nutrient intakes and fatty acid composition of serum lipids in patients with recently diagnosed non-insulin-dependant diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Spectrum 1995;8:102-3. - PubMed
Leinonen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Leinonen KS, Poutanen KS, Mykkanen HM. Rye bread decreases serum total and LDL cholesterol in men with moderately elevated serum cholesterol. Journal of Nutrition 2000;130:164-70. - PubMed
Lerman‐Garber 1995 {published data only}
-
- Lerman-Garber I, Gulias-Herrero A, Palma ME, Valles VE, Guerrero LA, Garcia EG, et al. Response to high carbohydrate and high monounsaturated fat diets in hypertriglyceridemic non-insulin dependent diabetic patients with poor glycemic control. Diabetes, Nutrition and Metabolism - Clinical and Experimental 1995;8:339-45.
Lieberman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Lieberman S. Natural methods for accelerating weight loss: the low glycemic index diet, green tea, chromium, and 5-hydroxytryptophan. Alternative and Complementary Therapies 2003;9(6):307-11.
Liu 2000 {published data only}
-
- Liu S, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Hu FB, Franz M, Sampson L, et al. A prospective study of dietary glycemic load, carbohydrate intake and risk of coronary heart disease in US women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2000;71(6):1455-61. - PubMed
Liu 2002 {published data only}
-
- Liu S, Manson JE, Buring JE, Stampfer MJ, Willett WC, Ridker PM. Relation between a diet with a high glycemic load and plasma concentrations of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in middle-aged women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;75(3):492-8. - PubMed
Ludwig 1999 {published data only}
-
- Ludwig DS, Majzoub JA, Al-Zahrani A, Dallal GE, Blanco I, Roberts SB. High glycemic index foods, overeating, and obesity. Pediatrics 1999;103(3):E26. - PubMed
Lunetta 1996 {published data only}
-
- Lunetta M, Mauro MD. Different effect of acute and chronic oral metformin administration on glucose and insulin response to bread and to pasta in non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 1996;33:53-8. - PubMed
Luscombe 1999 {published data only}
-
- Luscombe ND, Noakes M, Clifton PM. Diets high and low in glycemic index versus high monounsaturated fat diets: effects on glucose and lipid metabolism in NIDDM. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1999;53:473-8. - PubMed
Marsh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Marsh KA, Steinbeck KS, Atkinson FS, Petocz P, Brand-Miller JC. Effect of a low glycemic index compared with a conventional healthy diet on polycystic ovary syndrome. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92:83-92. - PubMed
Morales 1997 {published data only}
-
- Morales LM, Semprun-Fereira M, Ryder E, Valbuena H, Rincon E, Fernandez V, et al. Improved triglyceride control with low glycaemic index-high carbohydrate modified-lipid diet in a hypertriglyceridaemic child. Acta Paediatrica 1997;86:772-4. - PubMed
Nazare 2010 {published data only}
-
- Nazare JA, De Rougemont A, Normand S, Sauvinet V, Sothier M, Vinoy S, et al. Effect of postprandial modulation of glucose availability: short-and long-term analysis. British Journal of Nutrition 2010;103:1461-70. - PubMed
Pacy 1984 {published data only}
-
- Pacy PJ, Dodson PM, Kubicki AJ, Fletcher RF, Taylor KG. Effect of a high fibre, high carbohydrate dietary regimen on serum lipids and lipoproteins in type II hypertensive diabetic patients. Diabetes Research 1984;1:159-63. - PubMed
Patel 2004 {published data only}
-
- Patel VC, Aldridge RD, Leeds A, Dornhorst A, Frost GS. Retrospective analysis of the impact of a low glycaemic index diet on hospital stay following coronary artery bypass grafting: a hypothesis. Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics 2004;17(3):241-7. - PubMed
Patel 2011a {published data only}
Percheron 1997 {published data only}
-
- Percheron C, Colette C, Avignon A, Monnier L. Metabolic responses to high carbohydrate breakfasts in obese patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Comparison of meals containing dairy products and fruits versus bread. Nutrition Research 1997;17:797-806.
Pereira 2002 {published data only}
-
- Pereira MA, Jacobs DR, Pins JJ, Raatz SK, Gross MD, Slavin JL, et al. Effext of whole grains on insulin sensitivity in overweight hyperinsulinemic adults. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;75(5):848-55. - PubMed
Pereira 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pereira MA, Swain J, Goldfine AB, Rifai N, Ludwig DS. Effects of a low glycemic index load diet on resting energy expenditure and heart disease risk factors during weight loss. JAMA 2004;292(20):2482-90. - PubMed
Perichart‐Perera 2012 {published data only}
-
- Perichart-Perera O, Balas-Nakash M, Rodriguez-Cano A, Legorreta-Legorreta J, Parra-Covarrubias A, Vadillo-Ortega F. Low glycemic index carbohydrates versus all types of carbohydrates for treating diabetes in pregnancy: a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effect of glycemic control. International Journal of Endocrinology 2012;Epub 2012 Nov 29:296017. - PMC - PubMed
Pittas 2005 {published data only}
-
- Pittas AG, Das SK, Hajduk CL, Golden J, Saltzman E, Stark PC, et al. A low glycemic load diet facilitates greater weight loss in overweight adults with high insulin secretion but not in overweight adults with low insulin secretion in the CALERIE trial. Diabetes Care 2005;28(12):2939-41. - PubMed
Poppitt 2002 {published data only}
-
- Poppitt SD, Keogh GF, Prentice AM, Williams DEM, Sonnemans HMW, Valk EEJ, et al. Long-term effects of ad libitum low-fat, high-carbohydrate diets on body weight and serum lipids in overweight subjects with metabolic syndrome. American Society for Clinical Nutrition 2002;75:11-20. - PubMed
Rabasa‐Lhoret 1999 {published data only}
-
- Rabasa-Lhoret R, Garon J, Langelier H, Poisson D, Chiasson JL. Effects of meal carbohydrate content on insulin requirements in type 1 diabetic patients treated intensively with the basal-bolus (ultralente- regular) insulin regimen. Diabetes Care 1999;22:667-73. - PubMed
Rasmussen 1993 {published data only}
-
- Rasmussen OW, Thomsen C, Hansen KW, Vesterlund M, Winther E, Hermansen K. Effects on blood pressure, glucose, and lipid levels of a high-monounsaturated fat diet compared with a high-carbohydrate diet in NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care 1993;16:1564-71. - PubMed
Runchey 2012 {published data only}
Runchey 2013 {published data only}
Sacks 2013 {published data only}
-
- Sacks FM, Appel LJ, Carey VJ, Anderson CA, Charleston J, Copeland P, et al. Effect of dietary carbohydrate (amount and type) on risk factors for cardiovascular disease and diabetes: the omnicarb trial. Circulation 2013;127(Suppl 12):A016.
Salmeron 1997 {published data only}
-
- Salmeron J, Ascherio A, Rimm EB, Colditz GA, Spiegelman D, Jenkins DJ, et al. Dietary fiber, glycemic load, and risk of NIDDM in men. Diabetes Care 1997;20(4):545-50. - PubMed
Santacroce 1990 {published data only}
-
- Santacroce G, Forlani G, Giangiulio S, Galuppi V, Pagani M, Vannini P. Long-term effects of eating sucrose on metabolic control of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic outpatients. Acta Diabetologica Latina 1990;27:365-70. - PubMed
Scholz 2003 {published data only}
-
- Scholz S, Chantelau E. Glycemic index and insulin dosage on intensive insulin therapy [Glykämischer Index und Insulindosierung bei intensivierter Insulin-Therapie]. Interistische Praxis 2003;43(2):389-96.
Sciarrone 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sciarrone SEG, Martin T, Strahan LJ, Beilin VB, Burke V, Rogers P, et al. Ambulatory blood pressure and heart rate responses to vegetarian meals. Journal of Hypertension 1993;11:227-85. - PubMed
Sharafetdinov 1997 {published data only}
-
- Sharafetdinov KhKh, Meshcheriakova VA, Plotnikova OA. Change in postprandial glycemia as affected by various carbohydrate-containing products in patients with type II diabetes mellitus [Izmenenie poslepishchevoi glikemii pod vliianiem nekotorykh uglevodsoderzhashchikh produktov u bol'nykh sakharnym diabetom II tipa]. Voprosny Pitania 1997;1:27-30. - PubMed
Shikany 2009 {published data only}
Shyam 2013 {published data only}
Singh 1991 {published data only}
-
- Singh RB, Rastogi SS, Sircar AR, Mehta PJ, Sharma KK. Dietary strategies for risk factor modification to prevent cardiovascular diseases. Nutrition 1991;7:210-5. - PubMed
Slabber 1994 {published data only}
-
- Slabber M, Barnard HC, Kuyl JM, Dannhauser A, Schall R. Effects of a low-insulin response, energy restricted diet on weight loss and plasma insulin concentrations in hyperinsulinemic obese females. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994;60:48-53. - PubMed
Sloth 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sloth B, Krog-Mikkelson I, Flint A, Tetens I, Bjorck I, Vinoy S, et al. No difference in body weight decrease between a low-glycemic-index and a high-glycemic-index diet but reduced LDL cholesterol after 10-wk ad libitum intake of the low glycemic-index diet. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004;80:337-47. - PubMed
Spieth 2000 {published data only}
-
- Spieth LE, Harnish JD, Lenders CM, Raezer LB, Pereira MA, Hangen SJ, et al. A low glycemic index diet in the treatment of pediatric obesity. Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine 2000;154:947-51. - PubMed
Taghrid 2004 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Huet D, Rizkalla SW, Rigoir A, Veronese A, Pacher N, Slama G. Metabolic effects of chronic low glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2001;50(Suppl 2):A367.
-
- Rizkalla SW, Taghrid L, Laromiguiere M, Huet D, Boillot J, Rigoir A, et al. Improved plasma glucose control, whole-body glucose utilization, and lipid profile on a low-glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetic men: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2004;27(8):1866-72. - PubMed
-
- Taghrid L, Rizkalla SW, Huet D, Rigoir A, Veronese A, Slama G. Improvement of glycemic control and plasma lipid levels by chronic low glycemic index diet in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2003;52(Suppl 1):A72.
Tovar 2012 {published data only}
Tsihlias 2000 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Tsihlias EB, Gibbs AL, McBurney MI, Wolever TMS. Comparison of high-and low-glycemic index breakfast cereals with monounsaturated fat in the long-term dietary management of type 2 diabetes. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2000;72(2):439-49. - PubMed
Van Horn 1991 {published data only}
Visek 2011 {published data only}
-
- Visek J, Lacigova S, Cechurova D, Blaha V, Rusavy Z. Comparison of the impact of a low-glycemic index diet and a commonly used diabetic diet - a randomized crossover study. Clinical Nutrition Supplements 2011;6(1):117.
Vrolix 2010 {published data only}
-
- Vrolix R, Mensink RP. Effects of glycemic load on metabolic risk markers in subjects at increased risk of developing metabolic syndrome. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010;92:366-74. - PubMed
Wolever 1992a {published data only}
-
- Wolever TMS, Jenkins DJA, Vuksan V, Jenkins AL, Wong GS, Josse RG. Beneficial effect of low-glycemic index diet in overweight NIDDM subjects. Diabetes Care 1992;15(4):562-4. - PubMed
Wolever 1992b {published data only}
-
- Wolever TMS, Jenkins DJA, Vuksan V, Jenkins AL, Wong GS, Josse RG. Beneficial effect of low-glycaemic index diet in type 2 diabetes. Diabetic Medicine 1992;9:451-8. - PubMed
Wolever 1995 {published data only}
-
- Wolever T, Bentum-Williams AM, Jenkins DJA. Physiological modulation of plasma free fatty acid concenrations by diet: metabolic implications in nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 1995;18:962-70. - PubMed
Wolever 2008 {published data only}
-
- Wolever TM, Mehling C, Chiasson JL, Josse RG, Leiter LA, Maheux P, et al. Low glycaemic index diet and disposition index in type 2 diabetes (the Canadian trial of carbohydrates in diabetes): a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2008;51:1607-15. - PubMed
Yang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Yang EJ, Chung HK, Kim WY, Kerver JM, Song WO. Carbohydrate intake is associated with diet quality and risk factors for cardiovascular disease in US adults: NHANES III. Journal of the American College of Nutrition 2002;22:71-9. - PubMed
Yusof 2009 {published data only}
-
- Yusof BN, Talib RA, Kamaruddin NA, Karim NA, Chinna K, Gilbertson H. A low-GI diet is associated with a short-term improvement of glycaemic control in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism 2009;11:387-96. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Boyadjieva 2015 {published data only}
-
- Boyadjieva N, Handjieva-Darlenska T, Karamfilova V, Kamenov Z. No effect of glycemic index (low vs. high) on ghrelin and leptin in obesity. In: Obesity Facts. Vol. 8. 2015:39.
Cayanan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Cayanan E, Marhsall N, Yee B, Wong K, Djavadkhani Y, Grunstein R, Hoyos C. Effectiveness of two maintenance diets following a very low energy diet to reduce cardio-metabolic risk In obese sleep apnea patients: a randomized controlled trial. Sleep and Biological Rhythms 2015;13:56.
Giroux 2015 {published data only}
-
- Giroux I, Azzi S, Lavigne-Robichaud M, Comtois E, Blaine S, Whebby B, et al. The effect of a 6-month lifestyle education program on dietary behaviors in rural adults with prediabetes. In: Canadian Journal of Dietetic Practice & Research. Vol. 73. 2015:e2.
Karl 2015 {published data only}
References to ongoing studies
Brand‐Miller 2013 {published data only}
-
- Raben A, Fogelholm M, Feskens E, Westerterp-Plantenga M, Schlicht W, Brand-Miller J. PREVIEW: PREVention of diabetes through lifestyle Intervention and population studies in Europe and around the World. Obesity Facts 2013;6:194.
-
- Raben A, Fogelholm M, Larsen TM, Drummens M, Poppitt S, Formiguera JA, et al. PREVIEW: Prevention of diabetes through lifestyle intervention and population studies in Europe and around the world. Over 2,000 volunteers randomized to the 3-y RCT. In: Obesity Facts. Vol. 8. 2015:126.
-
- Silvestre M, Poppitt S, Liu A, Folgelholm M, Freskens E, Westerterp-Plantenga M, et al. PREVIEW: PREVention of diabetes through lifestyle Intervention in Europe and around the World – Where are we now? Obesity Research & Clinical Practice 2014;8:93-4.
Additional references
Aburto 2013
Atkinson 2008
Augustin 2015
-
- Augustin L, Kendall C, Jenkins D, Willett W, Astrup A, Barclay A, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load and glycemic response: an International Scientific Consensus Summit from the International Carbohydrate Quality Consortium (ICQC). Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2015;25(9):795-815. - PubMed
Barclay 2006
-
- Barclay AW, Brand-Miller JC. Validity of glycemic index estimates in the insulin resistance atherosclerosis study. Diabetes Care 2006;29(7):1718. - PubMed
Barclay 2008
-
- Barclay AW, Petocz P, McMillan-Price J, Flood VM, Prvan T, Mitchell P, et al. Glycemic index, glycemic load, and chronic disease risk - a meta-analysis of observational studies. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2008;87:627-37. - PubMed
BHF 2014
-
- Cardiovascular Disease 2014. www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/conditions/cardiovascular-disease.aspx (accessed January 2014).
Bjorck 2003
-
- Bjorck I, Elmstahl HL. The glycaemic index: importance of dietary fibre and other food properties. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2003;62(1):201-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Blaak 2012
Bornet 1987
-
- Bornet FR, Costagliola D, Rizkalla SW, Blayo A, Fontvielle AM, Haardt MJ, et al. Insulinemic and glycemic indexes of six starch-rich foods taken alone and in a mixed meal by type 2 diabetics. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1987;45:588-95. - PubMed
Bornet 2007
-
- Bornet FR, Jardy-Gennetier AE, Jacquet N, Stowell J. Glycaemic response to foods: impact on satiety and long-term weight regulation. Appetite 2007;49(3):535-53. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bovet 2012
-
- Bovet P, Paccaud F. Cardiovascular disease and the changing face of global public health: a focus on low and middle income countries. Public Health Reviews 2012;33(2):397-415.
Brand‐Miller 2002
-
- Brand-Miller JC, Holt SHA, Pawlak DB, McMillan J. Glycemic index and obesity. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;76(1):281S-5S. - PubMed
Coulston 1987
-
- Coulston AM, Hollenbeck CB, Swislocki AL, Reaven GM. Effect of source of dietary carbohydrate on plasma glucose and insulin responses to mixed meals in subjects with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1987;10:395-400. - PubMed
Dong 2012
-
- Dong JY, Zhang YH, Wang P, Qin LQ. Meta-analysis of dietary glycemic load and glycemic index in relation to risk of coronary heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology 2012;109(11):1608-13. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Du 2006
-
- Du H, Van der A DL, Feskens EJ. Dietary glycaemic index: a review of the physiological mechanisms and observed health impacts. Acta Cardiologica 2006;61(4):383-97. [PMID: ] - PubMed
FAO/WHO 1997
-
- FAO/WHO Expert Committee. Carbohydrates in Human Nutrition. FAO, 1998.
FAO/WHO 2007a
-
- Venn BJ, Green TJ. Glycemic index and glycemic load: measurement issues and their effect on diet–disease relationships. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;61 Suppl 1:S122–31. - PubMed
FAO/WHO 2007b
-
- Mann J, Cummings JH, Englyst HN, Key T, Liu S, Riccardi G, et al. FAO/WHO Scientific Update on carbohydrates in human nutrition: conclusions. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2007;61 Suppl 1:S132-7. - PubMed
Fleming 2013
-
- Fleming P, Godwin M. Low-glycaemic index diets in the management of blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Family Practice 2013;30(5):485-91. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Flint 2004
-
- Flint A, Moller BK, Raben A, Pedersen D, Tetens I, Holst JJ, et al. The use of glycaemic index tables to predict glycaemic index of composite breakfast meals. British Journal of Nutrition 2004;91:979-89. - PubMed
Follman 1992
-
- Follmann D, Elliot P, Suh I, Cutler J. Variance imputation for overviews of clinical trials with continuous response. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 1992;45(7):769-73. - PubMed
Ford 2001
-
- Ford ES, Liu S. Glycemic index and serum high density lipoprotein cholesterol concentration among US adults. Archives of Internal Medicine 2001;161:572-6. - PubMed
Foster‐Powell 1995
-
- Foster-Powell K, Miller JB. International tables of glycaemic index. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1995;62(4):871S-90S. - PubMed
Foster‐Powell 2002
-
- Foster-Powell K, Holt SH, Brand-Miller JB. International tables of glycemic index and glycemic load values. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;76:5-56. - PubMed
Frost 2000
-
- Frost G, Dornhorst A. The relevance of the glycaemic index to our understanding of dietary carbohydrates. Diabetic Medicine 2000;17:336-45. - PubMed
Goff 2013
-
- Goff LM, Cowland DE, Hooper L, Frost GS. Low glycaemic index diets and blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2013;23(1):1-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hu 2014
Jenkins 1981
-
- Jenkins D, Wolever T, Taylor H, Barker H, Fielden H, Baldwin AM, et al. Glycemic index of foods. A physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1981;34:362-6. - PubMed
Kristo 2013
Leeds 2002
-
- Leeds AR. Glycemic index and heart disease. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;76(1):286S-9S. - PubMed
Lefebvre 2011
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Ma 2012
-
- Ma XY, Liu JP, Song ZY. Glycemic load, glycemic index and risk of cardiovascular diseases: meta-analyses of prospective studies. Atherosclerosis 2012;223(2):491-6. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Meader 2014
Mirrahimi 2012
-
- Mirrahimi A, De Souza RJ, Chiavaroli L, Sievenpiper JL, Beyene J, Hanley AJ, et al. Associations of glycemic index and load with coronary heart disease events: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohorts. Journal of the American Heart Association 2012;1(5):e000752. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
NHS 2012
-
- National Health Service. Atherosclerosis 2012.. www.nhs.uk/conditions/Atherosclerosis/Pages/Introduction.aspx#commentCou... (accessed January 2014).
Niwano 2009
-
- Niwano Y, Adachi T, Kashimura J, Sakata T, Sasaki H, Sekine K, et al. Is glycemic index of food a feasible predictor of appetite, hunger, and satiety? Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology 2009;55(3):201-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Oude 2010
Rizkalla 2002
-
- Rizkalla SW, Bellisle F, Slama G. Health benefits of low glycaemic index foods, such as pulses, in diabetic patients and healthy individuals. British Journal of Nutrition 2002;88(Suppl 3):S255-S262. - PubMed
Spagnoli 2007
-
- Spagnoli LG, Bonanno E, Sangiorgi G, Mauriello A. Role of inflammation in atherosclerosis. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2007;48(11):1800-15. - PubMed
Thomas 2007
Thomas 2009
Vafeiadou 2012
-
- Vafeiadou K, Weech M, Sharma V, Yaqoob P, Todd S, Williams CM, et al. A review of the evidence for the effects of total dietary fat, saturated, monounsaturated and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids on vascular function, endothelial progenitor cells and microparticles. British Journal of Nutrition 2012;107(3):303-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
WHO 2013
-
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs317/en/index.html (accessed January 2014).
Wolever 1985
-
- Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ. Application of glycaemic index to mixed meals [letter]. Lancet 1985;2:944. - PubMed
Wolever 1986
-
- Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ. The use of the glycemic index in predicting the blood glucose response to mixed meals. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1986;43:167-72. - PubMed
Wolever 1988
-
- Wolever TM, Jenkins DJ, Collier GR, Lee R. Metabolic response to test meals containing different carbohydrate foods. 1. Relationship between rate of digestion and plasma insulin. Nutrition Reviews 1988;8:573-81.
Wolever 1990
-
- Wolever TM. The glycaemic index. World Review in Nutrition and Dietetics 1990;62:120-85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

