Risk Factors for a False-Negative Result of Sentinel Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node-Negative Breast Cancer
- PMID: 28759990
- PMCID: PMC6056988
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.089
Risk Factors for a False-Negative Result of Sentinel Node Biopsy in Patients with Clinically Node-Negative Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Although sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) can accurately represent the axillary lymph node (ALN) status, the false-negative rate (FNR) of SLNB is the main concern in the patients who receive SLNB alone instead of ALN dissection (ALND).
Materials and methods: We analyzed 1,886 patientswho underwent ALND after negative results of SLNB,retrospectively. A logistic regression analysis was used to identify risk factors associated with a falsenegative (FN) result. Cox regression model was used to estimate the hazard ratio of factors affecting disease-free survival (DFS).
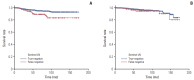
Results: Tumor located in the upper outer portion of the breast, lymphovascular invasion, suspicious node in imaging assessment and less than three sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) were significant independent risk factors for FN in SLNB conferring an adjusted odds ratio of 2.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.30 to 3.39), 2.69 (95% CI, 1.47 to 4.91), 2.59 (95% CI, 1.62 to 4.14), and 2.39 (95% CI, 1.45 to 3.95), respectively. The prognostic factors affecting DFS were tumor size larger than 2 cm (hazard ratio [HR], 1.86; 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.96) and FN of SLNB (HR, 2.51; 95% CI, 1.42 to 4.42) in SLN-negative group (FN and true-negative), but in ALN-positive group (FN and true-positive), FN of SLNB (HR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.33 to 1.25) did not affect DFS.
Conclusion: In patients with risk factors for a FN such as suspicious node in imaging assessment, upper outer breast cancer, less than three harvested nodes, we need attention to find another metastatic focus in non-SLNs during the operation. It may contribute to provide an exact prognosis and optimizing adjuvant treatments.
Keywords: Breast neoplasms; Prognosis; Sentinel lymph node; False negative.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures
References
-
- Mansel RE, Fallowfield L, Kissin M, Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Dixon JM, et al. Randomized multicenter trial of sentinel node biopsy versus standard axillary treatment in operable breast cancer: the ALMANAC Trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2006;98:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Paganelli G, Viale G, Luini A, Zurrida S, Galimberti V, et al. A randomized comparison of sentinel-node biopsy with routine axillary dissection in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:546–53. - PubMed
-
- Veronesi U, Viale G, Paganelli G, Zurrida S, Luini A, Galimberti V, et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer: ten-year results of a randomized controlled study. Ann Surg. 2010;251:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Costantino JP, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node resection compared with conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in clinically node-negative patients with breast cancer: overall survival findings from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:927–33. - PMC - PubMed
-
- van der Ploeg IM, Nieweg OE, van Rijk MC, Valdes Olmos RA, Kroon BB. Axillary recurrence after a tumour-negative sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008;34:1277–84. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous