PUREAIR protocol: randomized controlled trial of intensive pulmonary rehabilitation versus standard care in patients undergoing surgical resection for lung cancer
- PMID: 28760151
- PMCID: PMC5537935
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3479-y
PUREAIR protocol: randomized controlled trial of intensive pulmonary rehabilitation versus standard care in patients undergoing surgical resection for lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of lung cancer. Surgery is proven to be the most effective treatment in early stages, despite its potential impact on quality of life. Pulmonary rehabilitation, either before or after surgery, is associated with reduced morbidity related symptoms and improved exercise capacity, lung function and quality of life.
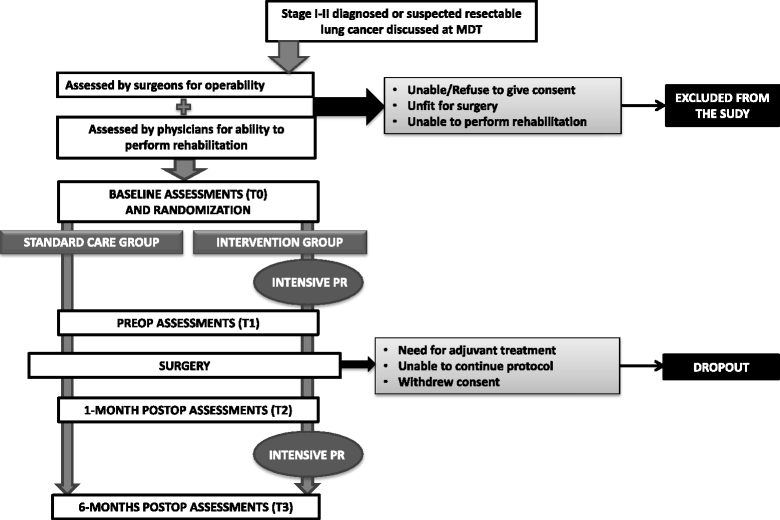
Methods: We describe the study protocol for the open-label randomized controlled trial we are conducting on patients affected by primary lung cancer (stages I-II) eligible for surgical treatment. The control group receives standard care consisting in one educational session before surgery and early inpatient postoperative physiotherapy. The treatment group receives, in addition to standard care, intensive rehabilitation involving 14 preoperative sessions (6 outpatient and 8 home-based) and 39 postoperative sessions (15 outpatient and 24 home-based) with aerobic, resistance and respiratory training, as well as scar massage and group bodyweight exercise training. Assessments are performed at baseline, the day before surgery and one month and six months after surgery. The main outcome is the long-term exercise capacity measured with the Six-Minute Walk Test; short-term exercise capacity, lung function, postoperative morbidity, length of hospital stay, quality of life (Short Form 12), mood disturbances (Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale) and pain (Numeric Rating Scale) are also recorded and analysed. Patient compliance and treatment-related side effects are also collected. Statistical analyses will be performed according to the intention-to-treat approach. T-test for independent samples will be used for continuous variables after assessment of normality of distribution. Chi-square test will be used for categorical variables. Expecting a 10% dropout rate, assuming α of 5% and power of 80%, we planned to enrol 140 patients to demonstrate a statistically significant difference of 25 m at Six-Minute Walk Test.
Discussion: Pulmonary Resection and Intensive Rehabilitation study (PuReAIR) will contribute significantly in investigating the effects of perioperative rehabilitation on exercise capacity, symptoms, lung function and long-term outcomes in surgically treated lung cancer patients. This study protocol will facilitate interpretation of future results and wide application of evidence-based practice.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Registry n. NCT02405273 [31.03.2015].
Keywords: Breathing exercises; Exercise therapy; Exercise tolerance; Lung neoplasms; Patient compliance; Patient education; Quality of life; Rehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the local Ethical Committee, at Arcispedale Santa Maria Nuova, IRCCS, Viale Umberto I n° 50, Reggio Emilia, on 9 April 2013 [n. 2013/0009390]. Written informed consent is obtained from participants by the operating surgeon during the preoperative consultation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rehabilitation for lung cancer patients undergoing surgery: results of the PUREAIR randomized trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021 Dec;57(6):1002-1011. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06789-7. Epub 2021 May 27. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021. PMID: 34042410 Clinical Trial.
-
Combined aerobic exercise and high-intensity respiratory muscle training in patients surgically treated for non-small cell lung cancer: a pilot randomized clinical trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019 Feb;55(1):113-122. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.18.05156-0. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2019. PMID: 29984565 Clinical Trial.
-
Preoperative pulmonary rehabilitation versus chest physical therapy in patients undergoing lung cancer resection: a pilot randomized controlled trial.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013 Jan;94(1):53-8. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2012.08.206. Epub 2012 Aug 24. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2013. PMID: 22926460 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Preoperative Breathing Exercise on Postoperative Outcomes for Patients With Lung Cancer Undergoing Curative Intent Lung Resection: A Meta-analysis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021 Dec;102(12):2416-2427.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2021.03.028. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33930327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of breathing exercises in subjects with lung cancer undergoing surgical resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Nurs. 2019 Mar;28(5-6):717-732. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14696. Epub 2018 Nov 20. J Clin Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30357997
Cited by
-
Feasibility of an eight-week outpatient-based pulmonary rehabilitation program for advanced lung cancer patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy in Korea.Thorac Cancer. 2018 Aug;9(8):1069-1073. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12788. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Thorac Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29932301 Free PMC article.
-
The correlation of preoperative six-minute walk distance and postoperative pneumonia after lung resection.J Thorac Dis. 2019 Jan;11(1):17-18. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.11.83. J Thorac Dis. 2019. PMID: 30863559 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Investigating the Physiological Mechanisms between Resistance Training and Pain Relief in the Cancer Population: A Literature Review.J Cancer Ther. 2023 Feb;14(2):80-101. doi: 10.4236/jct.2023.142008. Epub 2023 Feb 28. J Cancer Ther. 2023. PMID: 37502393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Union for International Cancer Control. Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer. 2014 Review of cancer medicines on the WHO list of essential medicines. WHO; 2014. http://www.who.int/selection_medicines/committees/expert/20/applications.... Accessed 15 Apr 2015.
-
- Cavalheri V, Tahirah F, Nonoyama M, Jenkins S, Hill K. Exercise training undertaken by people within 12 months of lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7:CD009955. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical