RNA-dependent stabilization of SUV39H1 at constitutive heterochromatin
- PMID: 28760200
- PMCID: PMC5538822
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.25299
RNA-dependent stabilization of SUV39H1 at constitutive heterochromatin
Abstract
Heterochromatin formed by the SUV39 histone methyltransferases represses transcription from repetitive DNA sequences and ensures genomic stability. How SUV39 enzymes localize to their target genomic loci remains unclear. Here, we demonstrate that chromatin-associated RNA contributes to the stable association of SUV39H1 with constitutive heterochromatin in human cells. We find that RNA associated with mitotic chromosomes is concentrated at pericentric heterochromatin, and is encoded, in part, by repetitive α-satellite sequences, which are retained in cis at their transcription sites. Purified SUV39H1 directly binds nucleic acids through its chromodomain; and in cells, SUV39H1 associates with α-satellite RNA transcripts. Furthermore, nucleic acid binding mutants destabilize the association of SUV39H1 with chromatin in mitotic and interphase cells - effects that can be recapitulated by RNase treatment or RNA polymerase inhibition - and cause defects in heterochromatin function. Collectively, our findings uncover a previously unrealized function for chromatin-associated RNA in regulating constitutive heterochromatin in human cells.
Keywords: SUV39H1; cell biology; chromatin; chromosomes; genes; heterochromatin; histone methylation; human; noncoding RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures
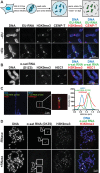

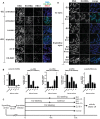
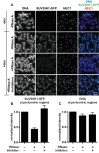
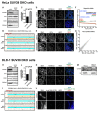
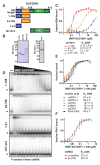
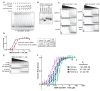
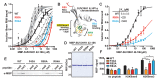

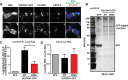
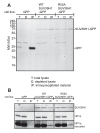
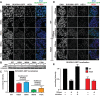
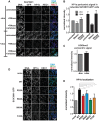
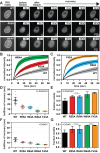

Comment in
-
Silencing repetitive DNA.Elife. 2017 Aug 1;6:e29503. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29503. Elife. 2017. PMID: 28760198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, Reuter G, Jenuwein T. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3-9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. The EMBO Journal. 1999;18:1923–1938. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.7.1923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

