TetR Family Transcriptional Regulator PccD Negatively Controls Propionyl Coenzyme A Assimilation in Saccharopolyspora erythraea
- PMID: 28760847
- PMCID: PMC5637179
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00281-17
TetR Family Transcriptional Regulator PccD Negatively Controls Propionyl Coenzyme A Assimilation in Saccharopolyspora erythraea
Abstract
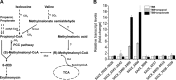
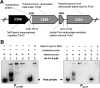
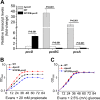
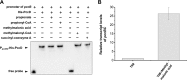
Propanol stimulates erythromycin biosynthesis by increasing the supply of propionyl coenzyme A (propionyl-CoA), a starter unit of erythromycin production in Saccharopolyspora erythraea Propionyl-CoA is assimilated via propionyl-CoA carboxylase to methylmalonyl-CoA, an extender unit of erythromycin. We found that the addition of n-propanol or propionate caused a 4- to 16-fold increase in the transcriptional levels of the SACE_3398-3400 locus encoding propionyl-CoA carboxylase, a key enzyme in propionate metabolism. The regulator PccD was proved to be directly involved in the transcription regulation of the SACE_3398-3400 locus by EMSA and DNase I footprint analysis. The transcriptional levels of SACE_3398-3400 were upregulated 15- to 37-fold in the pccD gene deletion strain (ΔpccD) and downregulated 3-fold in the pccD overexpression strain (WT/pIB-pccD), indicating that PccD was a negative transcriptional regulator of SACE_3398-3400. The ΔpccD strain has a higher growth rate than that of the wild-type strain (WT) on Evans medium with propionate as the sole carbon source, whereas the growth of the WT/pIB-pccD strain was repressed. As a possible metabolite of propionate metabolism, methylmalonic acid was identified as an effector molecule of PccD and repressed its regulatory activity. A higher level of erythromycin in the ΔpccD strain was observed compared with that in the wild-type strain. Our study reveals a regulatory mechanism in propionate metabolism and suggests new possibilities for designing metabolic engineering to increase erythromycin yield.IMPORTANCE Our work has identified the novel regulator PccD that controls the expression of the gene for propionyl-CoA carboxylase, a key enzyme in propionyl-CoA assimilation in S. erythraea PccD represses the generation of methylmalonyl-CoA through carboxylation of propionyl-CoA and reveals an effect on biosynthesis of erythromycin. This finding provides novel insight into propionyl-CoA assimilation, and extends our understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying the biosynthesis of erythromycin.
Keywords: erythromycin biosynthesis; propionate metabolism; propionyl-CoA assimilation; transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Wang W, Tian J, Li L, Ge M, Zhu H, Zheng G, Huang H, Ruan L, Jiang W, Lu Y. 2015. Identification of two novel regulatory genes involved in pristinamycin biosynthesis and elucidation of the mechanism for AtrA-p-mediated regulation in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:7151–7164. doi:10.1007/s00253-015-6638-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Feng R, Zheng G, Tian J, Ruan L, Ge M, Jiang W, Lu Y. 2015. Involvement of the TetR-type regulator PaaR in the regulation of pristinamycin I biosynthesis through an effect on precursor supply in Streptomyces pristinaespiralis. J Bacteriol 197:2062–2071. doi:10.1128/JB.00045-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

