Regulatory T-cells from pancreatic lymphnodes of patients with type-1 diabetes express increased levels of microRNA miR-125a-5p that limits CCR2 expression
- PMID: 28761107
- PMCID: PMC5537269
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-07172-1
Regulatory T-cells from pancreatic lymphnodes of patients with type-1 diabetes express increased levels of microRNA miR-125a-5p that limits CCR2 expression
Abstract
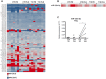
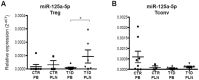
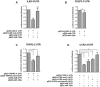
Autoimmune type 1 diabetes (T1D) is thought to be caused by a defective immune regulation with regulatory T (Treg) cells playing a fundamental role in this process. Tolerance mechanisms depend on tunable responses that are sensitive to minor perturbations in the expression of molecules that can be carried out by multiple epigenetic mechanisms, including regulation by microRNAs. In this study, microRNA expression profile was investigated in Treg cells isolated from peripheral blood (PB) and from pancreatic draining lymph nodes (PLN) of T1D patients and non-diabetic subjects. Among 72 microRNAs analyzed, miR-125a-5p resulted specifically hyper-expressed in Treg cells purified from PLN of T1D patients. TNFR2 and CCR2 were identified as miR-125a-5p target genes. Elevated miR-125a-5p was detected in Treg cells isolated from PLN but not from PB of donors with T1D and was associated with reduced CCR2 expression. A specific beta-cell expression of the CCR2-ligand (CCL2) was observed in the pancreata of cadaveric donors, suggesting that beta-cells are prone to attract CCR2+ Treg cells. These novel data propose a mechanism, occurring in PLNs of T1D patients, involving increased expression of miR-125a-5p on Treg cells which results into reduced expression of CCR2, thus limiting their migration and eventual function in the pancreas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

