A Comparative Study of Microneedling with Platelet-rich Plasma Plus Topical Minoxidil (5%) and Topical Minoxidil (5%) Alone in Androgenetic Alopecia
- PMID: 28761259
- PMCID: PMC5514790
- DOI: 10.4103/ijt.ijt_75_16
A Comparative Study of Microneedling with Platelet-rich Plasma Plus Topical Minoxidil (5%) and Topical Minoxidil (5%) Alone in Androgenetic Alopecia
Abstract
Context: There are very few studies evaluating efficacy of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in hair restoration and its combination with microneedling. As far as ascertained, there is no study to evaluate efficacy of microneedling with PRP plus topical minoxidil (5%) versus topical minoxidil (5%) alone in androgenetic alopecia (AGA).
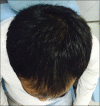
Aims: This study aims (1) to compare the efficacy of (a) topical minoxidil (5%) alone and (b) topical minoxidil (5%) + microneedling with PRP in men between 18 and 50 years with AGA Grade III to V vertex (Norwood-Hamilton scale) and (2) to perform objective and subjective evaluation based on clinical improvement and photographic evidence.
Settings and design: The study was conducted in the outpatient department of dermatology, venereology, and leprology in tertiary care hospital. It was open, prospective study.
Subjects and methods: Fifty patients with AGA were selected on the basis of inclusion and exclusion criteria. These patients were randomly divided into two groups of 25 patients each and were given following treatment: (i) Group A: topical minoxidil (5%) alone and (ii) Group B: topical minoxidil (5%) + microneedling with platelet-rich plasma (PRP).
Statistical analysis used: Patients were assessed before starting the treatment and at the end of 6 months on the basis of (a) Patient's self-assessment based on standardized seven-point scale compared with baseline (b) Physician's assessment based on standardized seven-point scale of hair growth compared with baseline.
Results: There was a significant improvement (P < 0.05) in both patients' assessment and investigator's assessment in Group B as compared to Group A at the end of 6 months.
Conclusions: Microneedling with PRP is safe, effective, and a promising tool for the management of AGA.
Keywords: Androgenetic alopecia; microneedling; minoxidil; platelet-rich plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Sinclair RD. Disorders of hair. In: Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Rook's Textbook of Dermatology. 8th ed. Vol. 4. UK: Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2010. pp. 66.16–66.31.
-
- Wadhwa SL, Khopkar U, Nischal KC. Hair and scalp disorders. In: Valia RG, Valia AR, editors. IADVL Textbook of Dermatology. 3rd ed. India: Bhalani Publishing House; 2008. pp. 887–94.
-
- Paus R, Oslen EA, Messenger AG. Hair growth disorders. In: Wolff K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffell DJ, editors. Fitzpatrick's Dermatology in General Medicine. 7th ed. USA: The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc; 2008. pp. 766–9.
-
- Vedamurthy M. Mesotherapy. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:60–2. - PubMed
-
- Escobar-Chávez JJ, Bonilla-Martínez D, Villegas-González MA, Molina-Trinidad E, Casas-Alancaster N, Revilla-Vázquez AL. Microneedles: A valuable physical enhancer to increase transdermal drug delivery. J Clin Pharmacol. 2011;51:964–77. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

