Efficacy of arthrocentesis versus arthrocentesis with sodium hyaluronic acid in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A comparison
- PMID: 28761275
- PMCID: PMC5512408
- DOI: 10.4103/njms.NJMS_84_16
Efficacy of arthrocentesis versus arthrocentesis with sodium hyaluronic acid in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: A comparison
Abstract
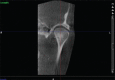
Introduction: Temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJ OA) is a degenerative disease characterized by deterioration of articular tissue with concomitant osseous changes in the condyle and/or articular eminence, joint positive for TMJ noise with jaw movement or function, crepitus detected on palpation on opening, closing, right/left lateral, or protrusive movement. Hyaluronic acid (HA) is a polysaccharide of the family of glycosaminoglycans. HA has been shown to improve and restore normal lubrication in joint, provide nutrition to the avascular articulating disc, and stabilize the joint.
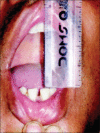
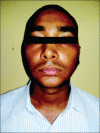
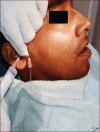
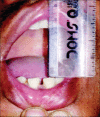
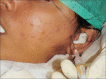
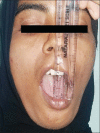
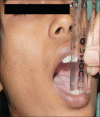
Materials and methods: Twenty patients with OA of TMJ with age limit between 18 and 60 years of age were enrolled in this study. Patients were randomly divided into two groups, in which one group received arthrocentesis only, and another group received arthrocentesis plus intra-articular injection of sodium HA (0.5 ml) in superior joint space in a cycle of 5 weekly arthrocentesis (one per week). Patients were followed at regular interval of 1st day, 5th day, 7th day, 4 weeks, 6 weeks, and 12 weeks. Assessment of clinical outcome was done in terms of reduction in pain (visual analog scale score), maximum mouth opening (MMO) in millimeters, painful/pain-free lateral or protrusive jaw movement, and clicking/crepitus in joint.
Results: Significant reduction in pain was observed in both the groups. MMO, lateral and protrusive movements improved significantly in both groups; however, arthrocentesis with sodium HA was superior to arthrocentesis alone.
Conclusion: Combination of arthrocentesis with HA injection showed much better outcome than arthrocentesis alone.
Keywords: Arthrocentesis; hyaluronic acid; osteoarthritis; temporomandibular joint.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





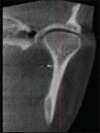
Similar articles
-
Combined Platelet-Rich Plasma and Hyaluronic Acid can Reduce Pain in Patients Undergoing Arthrocentesis for Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022 Sep;80(9):1474-1485. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2022.05.002. Epub 2022 May 16. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2022. PMID: 35679902 Clinical Trial.
-
Does intra-articular injection of tenoxicam after arthrocentesis heal outcomes of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis? A randomized clinical trial.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Mar 8;23(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-02852-z. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 36890529 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Does glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate, and methylsulfonylmethane supplementation improve the outcome of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis management with arthrocentesis plus intraarticular hyaluronic acid injection. A randomized clinical trial.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2021 Aug;49(8):711-718. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2021.02.012. Epub 2021 Feb 22. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33685850 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of platelet-rich plasma, platelet-rich growth factor with arthrocentesis or arthroscopy to treat temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis: Systematic review with meta-analyses.J Am Dent Assoc. 2018 Nov;149(11):940-952.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2018.07.025. J Am Dent Assoc. 2018. PMID: 30724168
-
Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid, Corticosteroids and Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7405. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147405. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299024 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Does Liquid/Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin Help in the Arthrocentesis Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Disorder Compared to Other Infusion Options? A Systematic Review of Randomized Clinical Trials.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Mar 2;11(3):247. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11030247. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Double-Needle Arthrocentesis with Viscosupplementation in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Disc Displacement without Reduction.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021 Apr 26;76:e2840. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2021/e2840. eCollection 2021. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2021. PMID: 33909828 Free PMC article.
-
Current Clinical Research Directions on Temporomandibular Joint Intra-Articular Injections: A Mapping Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jul 13;12(14):4655. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144655. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37510770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospective study to evaluate the influence of joint washing and the use of hyaluronic acid on 111 arthrocentesis.Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019 Dec;23(4):415-421. doi: 10.1007/s10006-019-00789-8. Epub 2019 Jul 1. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31264124
-
State of the Art in Temporomandibular Joint Arthrocentesis-A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 30;12(13):4439. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134439. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445474 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dworkin SF, LeResche L. Research diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders:Review, criteria, examinations and specifications, critique. J Craniomandib Disord. 1992;6:301–55. - PubMed
-
- Schiffman E, Ohrbach R, Truelove E, Look J, Anderson G, Goulet JP, et al. Diagnostic criteria for temporomandibular disorders (DC/TMD) for clinical and research applications: Recommendations of the international RDC/TMD consortium network* and orofacial pain special interest group†. J Oral Facial Pain Headache. 2014;28:6–27. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gadek A, Miskowiec K, Wordliczek J, Liszka H. Effectiveness and safety of intra-articular use of hyaluronic acid (Suplasyn) in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Przegl Lek. 2011;68:307–10. - PubMed
-
- Brusie RW, Sullins KE, White NA, 2nd, Coffin PC, Parker GA, Anver MR, et al. Evaluation of sodium hyaluronate therapy in induced septic arthritis in the horse. Equine Vet J Suppl. 1992;11:18–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

