Physicochemical characterization of drug nanocarriers
- PMID: 28761340
- PMCID: PMC5516877
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S133832
Physicochemical characterization of drug nanocarriers
Abstract
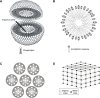
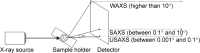
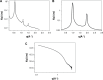
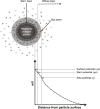
Pharmaceutical design has enabled important advances in the prevention, treatment, and diagnosis of diseases. The use of nanotechnology to optimize the delivery of drugs and diagnostic molecules is increasingly receiving attention due to the enhanced efficiency provided by these systems. Understanding the structures of nanocarriers is crucial in elucidating their physical and chemical properties, which greatly influence their behavior in the body at both the molecular and systemic levels. This review was conducted to describe the principles and characteristics of techniques commonly used to elucidate the structures of nanocarriers, with consideration of their size, morphology, surface charge, porosity, crystalline arrangement, and phase. These techniques include X-ray diffraction, small-angle X-ray scattering, dynamic light scattering, zeta potential, polarized light microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microcopy, and porosimetry. Moreover, we describe some of the commonly used nanocarriers (liquid crystals, metal-organic frameworks, silica nanospheres, liposomes, solid lipid nanoparticles, and micelles) and the main aspects of their structures.
Keywords: controlled drug release; drug delivery; nanoparticles; physicochemical properties.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

References
-
- Petros RA, DeSimone JM. Strategies in the design of nanoparticles for therapeutic applications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9(8):615–627. - PubMed
-
- Aznar E, Marcos MD, Martínez-Máñez R, et al. pH- and photo-switched release of guest molecules from mesoporous silica supports. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131(19):6833–6843. - PubMed
-
- Dong YD, Boyd BJ. Applications of X-ray scattering in pharmaceutical science. Int J Pharm. 2011;417(1–2):101–111. - PubMed
-
- Chang JH, Shim CH, Kim BJ, Shin Y, Exarhos GJ, Kim KJ. Bicontinuous, thermoresponsive, L3-phase silica nanocomposites and their smart drug-delivery applications. Adv Mater. 2005;17(5):634–637.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

