Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons through maintaining calbindin D28k immunoreactivity following subsequent transient cerebral ischemia
- PMID: 28761424
- PMCID: PMC5514866
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.208573
Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning on hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons through maintaining calbindin D28k immunoreactivity following subsequent transient cerebral ischemia
Abstract
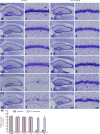
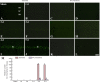
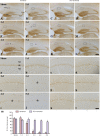
Ischemic preconditioning elicited by a non-fatal brief occlusion of blood flow has been applied for an experimental therapeutic strategy against a subsequent fatal ischemic insult. In this study, we investigated the neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning (2-minute transient cerebral ischemia) on calbindin D28k immunoreactivity in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 area following a subsequent fatal transient ischemic insult (5-minute transient cerebral ischemia). A large number of pyramidal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 area died 4 days after 5-minute transient cerebral ischemia. Ischemic preconditioning reduced the death of pyramidal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 area. Calbindin D28k immunoreactivity was greatly attenuated at 2 days after 5-minute transient cerebral ischemia and it was hardly detected at 5 days post-ischemia. Ischemic preconditioning maintained calbindin D28k immunoreactivity after transient cerebral ischemia. These findings suggest that ischemic preconditioning can attenuate transient cerebral ischemia-caused damage to the pyramidal neurons in the hippocampal CA1 area through maintaining calbindin D28k immunoreactivity.
Keywords: calcium binding protein; hippocampus; ischemic tolerance; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration; neuroprotection; pyramidal neurons; transient cerebral ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Bae EJ, Chen BH, Shin BN, Cho JH, Kim IH, Park JH, Lee JC, Tae HJ, Choi SY, Kim JD, Lee YL, Won MH, Ahn JH. Comparison of immunoreactivities of calbindin-D28k, calretinin and parvalbumin in the striatum between young, adult and aged mice, rats and gerbils. Neurochem Res. 2015;40:864–872. - PubMed
-
- Baimbridge KG, Celio MR, Rogers JH. Calcium-binding proteins in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1992;15:303–308. - PubMed
-
- Cai F, Liu J, Li C, Wang J. Intracellular calcium plays a critical role in the microcystin-LR-elicited neurotoxicity through PLC/IP3 pathway. Int J Toxicol. 2015;34:551–558. - PubMed
-
- D’Orlando C, Fellay B, Schwaller B, Salicio V, Bloc A, Gotzos V, Celio MR. Calretinin and calbindin D-28k delay the onset of cell death after excitotoxic stimulation in transfected P19 cells. Brain Res. 2001;909:145–158. - PubMed
-
- Fan Y, Shi L, Gu Y, Zhao Y, Xie J, Qiao J, Yang GY, Wang Y, Lu CZ. Pretreatment with PTD-calbindin D 28k alleviates rat brain injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007;27:719–728. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

