Evaluation of intermediate coronary stenoses in acute coronary syndromes using pressure guidewire
- PMID: 28761673
- PMCID: PMC5515130
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2016-000431
Evaluation of intermediate coronary stenoses in acute coronary syndromes using pressure guidewire
Abstract
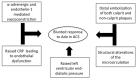
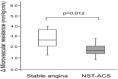
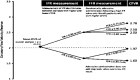
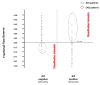
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) is increasingly used to guide myocardial revascularisation. However, supporting evidence regarding its use originates from studies that have enrolled mainly patients with stable angina, while patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) have not been included. Notably, multifactorial microvascular dysfunction and an increased sympathetic tone in patients with ACS may lead to blunted response to adenosine and false-negative results of FFR due to submaximal hyperaemia. This may raise the possibility of deferring treatment of stenosis that instead would have needed dilatation, thus leaving a residual risk of preventable cardiac events. In this literature review, we aim at summarising laboratory and clinical investigations concerning the use of FFR in culprit and non-culprit lesions in ACS. Furthermore, we will report recent data on instantaneous wave-free ratio, an adenosine-free index of functional stenosis severity, in stable coronary artery disease and in patients with ACS.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndromes; Fractional flow reserve; Instantaneous wave-free ratio.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Echavarría-Pinto M, van de Hoef TP, Serruys PW, et al. . Facing the complexity of ischaemic heart disease with intracoronary pressure and flow measurements: beyond fractional flow reserve interrogation of the coronary circulation. Curr Opin Cardiol 2014;29:564–70.10.1097/HCO.0000000000000110 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
