The influence of duloxetine on detrusor overactivity in rats with depression induced by 13-cis-retinoic acid
- PMID: 28762178
- PMCID: PMC6004276
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-017-3424-2
The influence of duloxetine on detrusor overactivity in rats with depression induced by 13-cis-retinoic acid
Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis: The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of duloxetine in an animal model of detrusor overactivity induced by depression.
Methods: After 6 weeks of 13-cis-retinoic acid administration at a dose of 1 mg/kg/day, rats were given duloxetine at a dose of 1 mg/kg. This was followed by conscious cystometry, a forced swim test, and locomotor activity measurement. The levels of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the hypothalamus, amygdala and plasma were also determined.
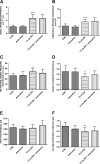
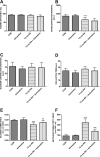
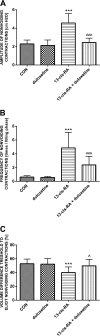
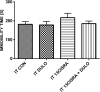
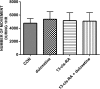
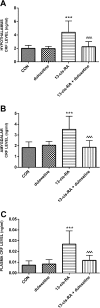
Results: Duloxetine treatment led to a reduction in detrusor overactivity symptoms induced by the retinoid. Decreases were observed in cystometric parameters including the detrusor overactivity index, and the amplitude and frequency of nonvoiding contractions, while increases were seen in bladder compliance and the volume threshold to elicit nonvoiding contractions. No statistically significant differences were found in basal pressure, threshold pressure, micturition voiding pressure, postvoid residual , volume threshold, voiding efficiency, intercontraction interval, bladder contraction duration or relaxation time. Duloxetine also reduced the immobility time to that observed in control animals, while it did not affect locomotor activity. Its effects also included lowering of the CRF levels in the hypothalamus, amygdala and plasma, which increased following the prior administration of the retinoid. The plasma level of 13-cis-retinoic acid in rats corresponded to the levels found in humans.
Conclusions: This is the first study showing the efficacy of duloxetine in an animal model of detrusor overactivity induced by depression. Further studies in patients with detrusor overactivity and coexisting depression are warranted to confirm these experimental results.
Keywords: Cystometry; Depression; Detrusor overactivity; Duloxetine; Rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding
This study was supported by Funds for Statutory Activity of the Medical University of Lublin, Poland.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An animal model of detrusor overactivity induced by depression.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016 Jul-Aug;80:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2016.04.001. Epub 2016 Apr 2. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27050558
-
SN003, a CRF1 receptor antagonist, attenuates depressive-like behavior and detrusor overactivity symptoms induced by 13-cis-retinoic acid in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Oct 5;812:216-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.07.010. Epub 2017 Jul 10. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28705713
-
The influence of Rho-kinase inhibition on acetic acid-induced detrusor overactivity.Neurourol Urodyn. 2017 Feb;36(2):263-270. doi: 10.1002/nau.22918. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Neurourol Urodyn. 2017. PMID: 26546786
-
Blebbistatin, a Myosin II Inhibitor, Exerts Antidepressant-Like Activity and Suppresses Detrusor Overactivity in an Animal Model of Depression Coexisting with Overactive Bladder.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):196-207. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9948-5. Epub 2018 Aug 28. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30155683 Free PMC article.
-
[Duloxetine and other tricyclic antidepressants: pharmacodynamic effects in the lower urinary tract].Actas Urol Esp. 2003 Nov-Dec;27(10):751-66. doi: 10.1016/s0210-4806(03)73012-5. Actas Urol Esp. 2003. PMID: 14735857 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Small compounds mimicking the adhesion molecule L1 improve recovery in a zebrafish demyelination model.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 15;11(1):5878. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85412-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33723325 Free PMC article.
-
New Kid on the Block: The Efficacy of Phytomedicine Extracts Urox® in Reducing Overactive Bladder Symptoms in Rats.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 21;9:896624. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.896624. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35801157 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Animal Models to Study Urinary Bladder Function.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 11;10(12):1316. doi: 10.3390/biology10121316. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychiatric History and Overactive Bladder Symptom Severity in Ambulatory Urogynecological Patients.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 3;10(17):3988. doi: 10.3390/jcm10173988. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34501436 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor used clinically, improves bladder function in a mouse model of moderate spinal cord injury.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Oct;16(10):2093-2098. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.308667. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33642399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engel WJ. Uropsychiatry. J Mich State Med Soc. 1964;63:273–277. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

