Perinatal high fat diet increases inhibition of dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurons regulating gastric functions
- PMID: 28762595
- PMCID: PMC5739938
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13150
Perinatal high fat diet increases inhibition of dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus neurons regulating gastric functions
Abstract
Background: Previous studies suggest an increased inhibition of dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV) neurons following exposure to a perinatal high fat diet (PNHFD); the underlying neural mechanisms, however, remain unknown. This study assessed the effects of PNHFD on inhibitory synaptic inputs to DMV neurons and the vagally dependent control of gastric tone and motility.
Methods: Whole-cell patch clamp recordings were made from DMV neurons in thin brainstem slices from Sprague-Dawley rats fed either a control diet or HFD (14 or 60% kcal from fat, respectively) from embryonic day 13 onwards; gastric tone and motility were recorded in in vivo anesthetized rats.
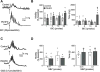
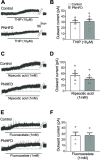
Key results: The non-selective GABAA antagonist, BIC (10 μmol L-1 ), induced comparable inward currents in PNHFD and control DMV neurons, but a larger current in PNHFD neurons at higher concentrations (50 μmol L-1 ). Differences were not apparent in neuronal responses to the phasic GABAA antagonist, gabazine (GBZ), the extrasynaptic GABAA agonist, THIP, the GABA transport blocker, nipecotic acid, or the gliotoxin, fluoroacetate, suggesting that PNHFD altered inhibitory transmission but not GABAA receptor density or function, GABA uptake or glial modulation of synaptic strength. Similarly, the increase in gastric motility and tone following brainstem microinjection of low doses of BIC (1-10 pmoles) and GBZ (0.01-0.1 pmoles) were unchanged in PNHFD rats while higher doses of BIC (25 pmoles) induced a significantly larger increase in gastric tone compared to control.
Conclusions and inferences: These studies suggest that exposure to PNHFD increases the tonic inhibition of DMV neurons, possibly contributing to dysregulated vagal control of gastric functions.
Keywords: DMV; GABA receptors; gastric motility; perinatal high fat diet.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
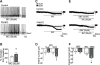

Similar articles
-
Perinatal high-fat diet alters development of GABAA receptor subunits in dorsal motor nucleus of vagus.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):G40-G50. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00079.2019. Epub 2019 May 1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31042399 Free PMC article.
-
Sex differences in GABAergic neurotransmission to rat DMV neurons.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Oct 1;317(4):G476-G483. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00112.2019. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31393788 Free PMC article.
-
Acute high-fat diet upregulates glutamatergic signaling in the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 May 1;314(5):G623-G634. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00395.2017. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29368945 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem Neuronal Circuitries Controlling Gastric Tonic and Phasic Contractions: A Review.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Mar;42(2):333-360. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01084-5. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33813668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasticity of vagal brainstem circuits in the control of gastrointestinal function.Auton Neurosci. 2011 Apr 26;161(1-2):6-13. doi: 10.1016/j.autneu.2010.11.001. Epub 2010 Dec 13. Auton Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21147043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perinatal high-fat diet alters development of GABAA receptor subunits in dorsal motor nucleus of vagus.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019 Jul 1;317(1):G40-G50. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00079.2019. Epub 2019 May 1. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31042399 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamatergic plasticity within neurocircuits of the dorsal vagal complex and the regulation of gastric functions.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):G880-G887. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00014.2021. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33730858 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DMV extrasynaptic NMDA receptors regulate caloric intake in rats.JCI Insight. 2021 May 10;6(9):e139785. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.139785. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33764905 Free PMC article.
-
Brainstem astrocytes control homeostatic regulation of caloric intake.J Physiol. 2023 Feb;601(4):801-829. doi: 10.1113/JP283566. Epub 2023 Jan 25. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36696965 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Kinase C-Dependent Effects of Neurosteroids on Synaptic GABAA Receptor Inhibition Require the δ-Subunit.Front Physiol. 2021 Oct 25;12:742838. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.742838. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34759836 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

