Edwardsiella tarda-induced miRNAs in a teleost host: Global profile and role in bacterial infection as revealed by integrative miRNA-mRNA analysis
- PMID: 28762875
- PMCID: PMC5711354
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2017.1356541
Edwardsiella tarda-induced miRNAs in a teleost host: Global profile and role in bacterial infection as revealed by integrative miRNA-mRNA analysis
Keywords: Cynoglossus semilaevis; Edwardsiella tarda; immune defense; infection; miRNA.
Figures
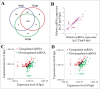

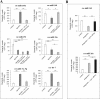
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of the expression patterns of eight suppressors of cytokine signaling in tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016 Aug;55:595-601. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2016.06.034. Epub 2016 Jun 23. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27346156
-
Identification and Characterization of Long Non-coding RNAs in the Intestine of Olive Flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) During Edwardsiella tarda Infection.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 31;12:623764. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623764. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868240 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and expression analysis of nine CC chemokines in half-smooth tongue sole, Cynoglossus semilaevis.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015 Dec;47(2):717-24. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26470888
-
Multiplex PCR assay for correct identification of the fish pathogenic species of Edwardsiella genus reveals the presence of E. anguillarum in South America in strains previously characterized as E. tarda.J Appl Microbiol. 2022 Jun;132(6):4225-4235. doi: 10.1111/jam.15538. Epub 2022 Apr 4. J Appl Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35332638 Review.
-
Edwardsiella piscicida: a significant bacterial pathogen of cultured fish.Dis Aquat Organ. 2018 Oct 16;131(1):59-71. doi: 10.3354/dao03281. Dis Aquat Organ. 2018. PMID: 30324915 Review.
Cited by
-
A Novel microRNA of Japanese Flounder Regulates Antimicrobial Immunity Involving a Bacteria-Binding CSF3.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 19;12:723401. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.723401. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34489973 Free PMC article.
-
Interwoven processes in fish development: microbial community succession and immune maturation.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 27;12:e17051. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17051. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38560465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs Function as Immune Regulators in Teleost Fish.Front Immunol. 2018 Nov 28;9:2801. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02801. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30546368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal Gene Expression Signature of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles-MicroRNAs from Post-Smolt Coho Salmon Challenged with Piscirickettsia salmonis.Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2021 Aug;23(4):602-614. doi: 10.1007/s10126-021-10049-0. Epub 2021 Aug 14. Mar Biotechnol (NY). 2021. PMID: 34390423
-
Micro-Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Immune-Related MicroRNA Regulatory Networks of Paralichthys olivaceus Induced by Vibrio anguillarum Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4252. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124252. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Janda JM, Abbott SL. Infections associated with the genus Edwardsiella: the role of Edwardsiella tarda in human disease. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 17:742-48. PMID:8268359 http://www.jstor.org/stable/4457376 - PubMed
-
- Mohanty BR, Sahoo PK. Edwardsiellosis in fish: a brief review. J Biosci. 2007; 32(7):1331-44 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
