Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies
- PMID: 28762997
- PMCID: PMC5577590
- DOI: 10.3390/md15080235
Investigating the Biosynthesis of Natural Products from Marine Proteobacteria: A Survey of Molecules and Strategies
Abstract
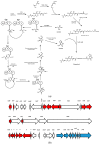
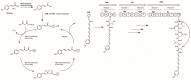
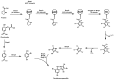
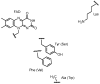
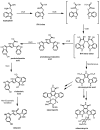
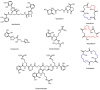
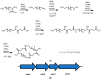
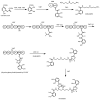
The phylum proteobacteria contains a wide array of Gram-negative marine bacteria. With recent advances in genomic sequencing, genome analysis, and analytical chemistry techniques, a whole host of information is being revealed about the primary and secondary metabolism of marine proteobacteria. This has led to the discovery of a growing number of medically relevant natural products, including novel leads for the treatment of multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and cancer. Of equal interest, marine proteobacteria produce natural products whose structure and biosynthetic mechanisms differ from those of their terrestrial and actinobacterial counterparts. Notable features of secondary metabolites produced by marine proteobacteria include halogenation, sulfur-containing heterocycles, non-ribosomal peptides, and polyketides with unusual biosynthetic logic. As advances are made in the technology associated with functional genomics, such as computational sequence analysis, targeted DNA manipulation, and heterologous expression, it has become easier to probe the mechanisms for natural product biosynthesis. This review will focus on genomics driven approaches to understanding the biosynthetic mechanisms for natural products produced by marine proteobacteria.
Keywords: biosynthesis; genomics; natural products; proteobacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

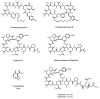

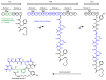
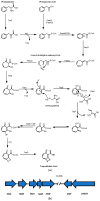
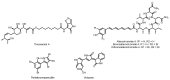
Similar articles
-
Marine Proteobacteria as a source of natural products: advances in molecular tools and strategies.Nat Prod Rep. 2019 Sep 1;36(9):1333-1350. doi: 10.1039/c9np00020h. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Nat Prod Rep. 2019. PMID: 31490501 Review.
-
Marine Microbial Secondary Metabolites: Pathways, Evolution and Physiological Roles.Adv Microb Physiol. 2015;66:357-428. doi: 10.1016/bs.ampbs.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 30. Adv Microb Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26210108 Review.
-
Utilizing the power of microbial genetics to bridge the gap between the promise and the application of marine natural products.Chembiochem. 2005 Jun;6(6):960-78. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200400428. Chembiochem. 2005. PMID: 15880675 Review.
-
Genome mining as a biotechnological tool for the discovery of novel marine natural products.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020 Aug;40(5):571-589. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2020.1751056. Epub 2020 Apr 19. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32308042 Review.
-
Bacterial biosynthesis and maturation of the didemnin anti-cancer agents.J Am Chem Soc. 2012 May 23;134(20):8625-32. doi: 10.1021/ja301735a. Epub 2012 Apr 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2012. PMID: 22458477 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Diversity and Distribution of Bacteria Producing Known Secondary Metabolites.Microb Ecol. 2019 Nov;78(4):885-894. doi: 10.1007/s00248-019-01380-0. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Microb Ecol. 2019. PMID: 31016338
-
Individual Physiological Adaptations Enable Selected Bacterial Taxa To Prevail during Long-Term Incubations.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019 Jul 18;85(15):e00825-19. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00825-19. Print 2019 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31152013 Free PMC article.
-
High Potential for Secondary Metabolite Production of Paracoccus marcusii CP157, Isolated From the Crustacean Cancer pagurus.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 28;12:688754. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.688754. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34262548 Free PMC article.
-
The Tripod for Bacterial Natural Product Discovery: Genome Mining, Silent Pathway Induction, and Mass Spectrometry-Based Molecular Networking.mSystems. 2018 Mar 27;3(2):e00160-17. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00160-17. eCollection 2018 Mar-Apr. mSystems. 2018. PMID: 29629418 Free PMC article.
-
Marine Biotechnology: Challenges and Development Market Trends for the Enhancement of Biotic Resources in Industrial Pharmaceutical and Food Applications. A Statistical Analysis of Scientific Literature and Business Models.Mar Drugs. 2021 Jan 26;19(2):61. doi: 10.3390/md19020061. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33530360 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Davies J.C., Alton E.W., Bush A. Cystic fibrosis. Br. Med. J. 2007;335:1255–1259. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39391.713229.AD. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

