The Linoleic Acid: Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid Ratio (LA:DGLA)-An Emerging Biomarker of Zn Status
- PMID: 28763004
- PMCID: PMC5579618
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9080825
The Linoleic Acid: Dihomo-γ-Linolenic Acid Ratio (LA:DGLA)-An Emerging Biomarker of Zn Status
Abstract
Zinc (Zn) deficiency is a common aliment predicted to affect 17% of the world's population. Zinc is a vital micronutrient used for over 300 enzymatic reactions and multiple biochemical and structural processes in the body. Although whole blood, plasma, and urine zinc decrease in severe zinc deficiency, accurate assessment of zinc status, especially in mild to moderate deficiency, is difficult as studies with these biomarkers are often contradictory and inconsistent. Hence, as suggested by the World Health Organization, sensitive and specific biological markers of zinc status are still needed. In this review, we provide evidence to demonstrate that the LA:DGLA ratio (linoleic acid:dihomo-γ-linolenic acid ratio) may be a useful additional indicator for assessing Zn status more precisely. However, this biomarker needs to be tested further in order to determine its full potential.
Keywords: LA:DGLA; Zn; Zn status; biomarker; fatty acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
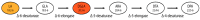

References
-
- Prasad A.S., Schulert A.R., Miale A., Farid Z., Sanstead H.H. Zinc and iron deficiencies in male subjects with dwarfism and hypogonadism but without ancylostomiasis, schistosomiasis or severe anemia. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1963;12:437–444. - PubMed
-
- King J.C., Cousins R.J. Zinc. In: Shils M.E., Shike M., editors. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease. 10th ed. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; Baltimore, MD, USA: 2006. pp. 271–285.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

