Metal Binding Properties of the N-Terminus of the Functional Amyloid Orb2
- PMID: 28763009
- PMCID: PMC5618238
- DOI: 10.3390/biom7030057
Metal Binding Properties of the N-Terminus of the Functional Amyloid Orb2
Abstract
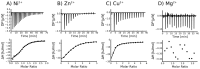
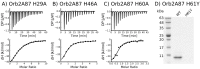
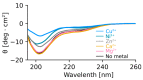
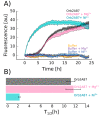
The cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein (CPEB) homologue Orb2 is a functional amyloid that plays a key regulatory role for long-term memory in Drosophila. Orb2 has a glutamine, histidine-rich (Q/H-rich) domain that resembles the Q/H-rich, metal binding domain of the Hpn-like protein (Hpnl) found in Helicobacter pylori. In the present study, we used chromatography and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) to show that the Q/H-rich domain of Orb2 binds Ni2+ and other transition metals ions with μM affinity. Using site directed mutagenesis, we show that several histidine residues are important for binding. In particular, the H61Y mutation, which was previously shown to affect the aggregation of Orb2 in cell culture, completely inhibited metal binding of Orb2. Finally, we used thioflavin T fluorescence and electron microscopy images to show that Ni2+ binding induces the aggregating of Orb2 into structures that are distinct from the amyloid fibrils formed in the absence of Ni2+. These data suggest that transition metal binding might be important for the function of Orb2 and potentially long-term memory in Drosophila.
Keywords: ITC; aggregation; amyloid; protein–metal interaction; thioflavin T fluorescence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification and Structural Characterization of the N-terminal Amyloid Core of Orb2 isoform A.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 6;6:38265. doi: 10.1038/srep38265. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27922050 Free PMC article.
-
Droplet and fibril formation of the functional amyloid Orb2.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul;297(1):100804. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100804. Epub 2021 May 25. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34044018 Free PMC article.
-
Micro-electron diffraction structure of the aggregation-driving N terminus of Drosophila neuronal protein Orb2A reveals amyloid-like β-sheets.J Biol Chem. 2022 Oct;298(10):102396. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102396. Epub 2022 Aug 18. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35988647 Free PMC article.
-
Implications of the Orb2 Amyloid Structure in Huntington's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 21;21(18):6910. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186910. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32967102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding proteins in development, health, and disease.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014;30:393-415. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-101011-155831. Epub 2014 Jul 14. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 25068488 Review.
Cited by
-
A new era for understanding amyloid structures and disease.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Dec;19(12):755-773. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0060-8. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 30237470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncovering the universality of self-replication in protein aggregation and its link to disease.Sci Adv. 2022 Aug 12;8(32):eabn6831. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn6831. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35960802 Free PMC article.
-
Structural transitions in Orb2 prion-like domain relevant for functional aggregation in memory consolidation.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 25;295(52):18122-18133. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.015211. Epub 2020 Oct 22. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33093173 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Si K., Giustetto M., Etkin A., Hsu R., Janisiewicz A.M., Miniaci M.C., Kim J.-H., Zhu H., Kandel E.R. A neuronal isoform of CPEB regulates local protein synthesis and stabilizes synapse-specific long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Cell. 2003;115:893–904. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)01021-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

