Health Care Expenditures and Utilization for Children With Noncomplex Chronic Disease
- PMID: 28765382
- PMCID: PMC7024918
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2017-0492
Health Care Expenditures and Utilization for Children With Noncomplex Chronic Disease
Abstract
Background: Pediatric health care expenditures and use vary by level of complexity and chronic illness. We sought to determine expenditures and use for children with noncomplex chronic diseases (NC-CDs).
Methods: We performed a retrospective, cross-sectional analysis of Medicaid enrollees (ages 0-18 years) from January 1, 2012, through December 31, 2013, using administrative claims (the Truven MarketScan Medicaid Database). Patients were categorized by chronicity of illness by using 3M Health Information System's Clinical Risk Groups (CRGs) as follows: without chronic diseases (WO-CDs) (CRG 1-2), NC-CDs (CRG 3-5), and complex chronic diseases (C-CDs) (CRG 6-9). Primary outcomes were medical expenditures, including total annualized population expenditure and per-member per-year expenditure (PMPY). Secondary outcomes included the number of health care encounters over the 2-year period.
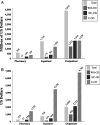
Results: There were 2 424 946 children who met inclusion criteria, 53% were WO-CD; 36% had an NC-CD; and 11% had a C-CD. Children with NC-CDs accounted for 33% ($2801 PMPY) of the annual spending compared with 20% ($1151 PMPY) accounted for by children WO-CDs and 47% ($12 569 PMPY) by children with C-CDs. The median outpatient visit count by group over the 2-year period was 15 (interquartile range [IQR] 10-25) for NC-CD, 8 (IQR 5-13) WO-CD, and 34 (IQR 19-72) for C-CD.
Conclusions: Children with NC-CDs accounted for 33% of pediatric Medicaid expenditures and have significantly higher PMPY and aggregate annual expenditures than children WO-CDs. The annual aggregate expenditures of the NC-CD group represent a significant societal cost because of the high volume of children, extrapolated to ∼$34.9 billion annually in national Medicaid expenditures.
Copyright © 2017 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Simon TD, Cawthon ML, Stanford S, et al. ; Center of Excellence on Quality of Care Measures for Children with Complex Needs (COE4CCN) Medical Complexity Working Group . Pediatric medical complexity algorithm: a new method to stratify children by medical complexity. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6). Available at: www.pediatrics.org/cgi/content/full/133/6/e1647 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Froehlich TE, Lanphear BP, Epstein JN, Barbaresi WJ, Katusic SK, Kahn RS. Prevalence, recognition, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in a national sample of US children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2007;161(9):857–864 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

