Antigen-specific regulatory T-cell responses to intestinal microbiota
- PMID: 28766556
- PMCID: PMC5939566
- DOI: 10.1038/mi.2017.65
Antigen-specific regulatory T-cell responses to intestinal microbiota
Abstract
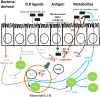
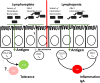
The mammalian gastrointestinal tract can harbor both beneficial commensal bacteria important for host health, but also pathogenic bacteria capable of intestinal damage. It is therefore important that the host immune system mount the appropriate immune response to these divergent groups of bacteria-promoting tolerance in response to commensal bacteria and sterilizing immunity in response to pathogenic bacteria. Failure to induce tolerance to commensal bacteria may underlie immune-mediated diseases such as human inflammatory bowel disease. At homeostasis, regulatory T (Treg) cells are a key component of the tolerogenic response by adaptive immunity. This review examines the mechanisms by which intestinal bacteria influence colonic T-cells and B-cell immunoglobulin A (IgA) induction, with an emphasis on Treg cells and the role of antigen-specificity in these processes. In addition to discussing key primary literature, this review highlights current controversies and important future directions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gilbert JA, Quinn RA, Debelius J, Xu ZZ, Morton J, Garg N, et al. Microbiome-wide association studies link dynamic microbial consortia to disease. Nature. 2016;535(7610):94–103. - PubMed
-
- Flint HJ, Scott KP, Louis P, Duncan SH. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;9(10):577–589. - PubMed
-
- Blanton LV, Barratt MJ, Charbonneau MR, Ahmed T, Gordon JI. Childhood undernutrition, the gut microbiota, and microbiota-directed therapeutics. Science. 2016;352(6293):1533. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

