Influence of oxygen content immediately after graft reperfusion on occurrence of postoperative acute kidney injury in living donor liver transplantation
- PMID: 28767577
- PMCID: PMC5626131
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007626
Influence of oxygen content immediately after graft reperfusion on occurrence of postoperative acute kidney injury in living donor liver transplantation
Abstract
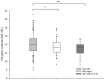
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication after living donor liver transplantation (LDLT). In this study, we investigated perioperative factors, including oxygen content, related to the postoperative development of AKI after LDLT. The perioperative data of 334 patients were reviewed retrospectively. We identified the postoperative development of AKI based on the Acute Kidney Injury Network criteria. Perioperative variables, including oxygen content, were compared between patients with and without AKI. Potentially significant variables in a univariate analysis were evaluated by multivariate analysis. Postoperative AKI developed in 76 patients (22.7%). Univariate analysis revealed that preoperative factors (body mass index [BMI], diabetes mellitus, C-reactive protein) and intraoperative factors (severe postreperfusion syndrome, packed red blood cell transfusion, furosemide, and oxygen content at the anhepatic phase, 5 minutes and 1 hour after graft reperfusion, and at peritoneal closure) of recipients were significant. The multivariate analysis showed that oxygen content 5 minutes after graft reperfusion, BMI, and furosemide administration were independently associated with postoperative AKI. In conclusion, postoperative AKI was independently associated with oxygen content 5 minutes after graft reperfusion, BMI, and furosemide administration. Meticulous ventilator care and transfusion should be required to maintain sufficient oxygen content immediately after graft reperfusion in patients who undergo LDLT.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Barri YM, Sanchez EQ, Jennings LW, et al. Acute kidney injury following liver transplantation: definition and outcome. Liver Transpl 2009;15:475–83. - PubMed
-
- Hilmi IA, Damian D, Al-Khafaji A, et al. Acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: incidence, risk factors, and effects on patient and graft outcomes. Br J Anaesth 2015;114:919–26. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Park JB, Kim SJ, et al. Early postoperative renal dysfunction in the adult living donor liver transplantation. Transplant Proc 2007;39:1517–9. - PubMed
-
- Leithead JA, Rajoriya N, Gunson BK, et al. The evolving use of higher risk grafts is associated with an increased incidence of acute kidney injury after liver transplantation. J Hepatol 2014;60:1180–6. - PubMed
-
- Leithead JA, Armstrong MJ, Corbett C, et al. Hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury is associated with acute kidney injury following donation after brain death liver transplantation. Transpl Int 2013;26:1116–25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

