Carbon monoxide released from its pharmacological donor, tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer, accelerates the healing of pre-existing gastric ulcers
- PMID: 28768046
- PMCID: PMC5610153
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.13968
Carbon monoxide released from its pharmacological donor, tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer, accelerates the healing of pre-existing gastric ulcers
Abstract
Background and purpose: Carbon monoxide (CO), a gaseous mediator produced by haem oxygenases (HOs), has been shown to prevent stress-, ethanol-, aspirin- and alendronate-induced gastric damage; however, its role in gastric ulcer healing has not been fully elucidated. We investigated whether CO released from tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer (CORM-2) can affect gastric ulcer healing and determined the mechanisms involved in this healing action.
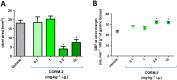
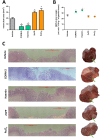
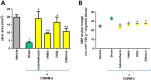
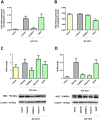
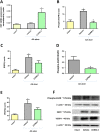
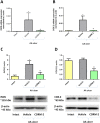
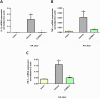
Experimental approach: Gastric ulcers were induced in Wistar rats by serosal application of acetic acid. Animals received 9 days of treatment with RuCl3 [2.5 mg·kg-1 intragastrically (i.g.)], haemin (5 mg·kg-1 i.g.), CORM-2 (0.1-10 mg·kg-1 i.g.) administered alone or with zinc protoporphyrin IX (ZnPP, 10 mg·kg-1 i.g.), 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ, 5 mg·kg-1 i.g.), NG -nitro-l-arginine (l-NNA, 15 mg·kg-1 i.g.), indomethacin (5 mg·kg-1 i.g.) or glibenclamide (10 mg·kg-1 i.g.). Gastric ulcer area and gastric blood flow (GBF) were assessed planimetrically, microscopically and by laser flowmeter respectively. Gastric mRNA/protein expressions of EGF, EGF receptors, VEGFA, HOs, nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (Nrf2), COX-2, hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α and pro-inflammatory iNOS, IL-1β and TNF-α were determined by real-time PCR or Western blots.
Key results: CORM-2 and haemin but not RuCl3 or ZnPP decreased ulcer size while increasing GBF. These effects were reduced by ODQ, indomethacin, l-NNA and glibenclamide. CORM-2 significantly decreased the expression of pro-inflammatory markers, Nrf2/HO1 and HIF-1α, and up-regulated EGF.
Conclusions and implications: CO released from CORM-2 or endogenously produced by the HO1/Nrf2 pathway accelerates gastric ulcer healing via an increase in GBF, an up-regulation in EGF expression and down-regulation of the inflammatory response.
© 2017 The British Pharmacological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Bucci M, Papapetropoulos A, Vellecco V, Zhou Z, Zaid A, Giannogonas P et al (2012). cGMP‐dependent protein kinase contributes to hydrogen sulfide‐stimulated vasorelaxation. PLoS One 7: e53319, https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0053319. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cacanyiova S, Berenyiova A, Kristek F, Drobna M, Ondrias K, Grman M (2016). The adaptive role of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulphide in vasoactive responses of thoracic aorta is triggered already in young spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Physiol Pharmacol 67: 501–512. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

