Loss of Brain Aerobic Glycolysis in Normal Human Aging
- PMID: 28768174
- PMCID: PMC5573225
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.010
Loss of Brain Aerobic Glycolysis in Normal Human Aging
Abstract
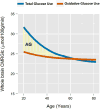
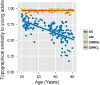
The normal aging human brain experiences global decreases in metabolism, but whether this affects the topography of brain metabolism is unknown. Here we describe PET-based measurements of brain glucose uptake, oxygen utilization, and blood flow in cognitively normal adults from 20 to 82 years of age. Age-related decreases in brain glucose uptake exceed that of oxygen use, resulting in loss of brain aerobic glycolysis (AG). Whereas the topographies of total brain glucose uptake, oxygen utilization, and blood flow remain largely stable with age, brain AG topography changes significantly. Brain regions with high AG in young adults show the greatest change, as do regions with prolonged developmental transcriptional features (i.e., neoteny). The normal aging human brain thus undergoes characteristic metabolic changes, largely driven by global loss and topographic changes in brain AG.
Keywords: aerobic glycolysis; brain aging; brain metabolism; neoteny.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Holding Onto Youth.Cell Metab. 2017 Aug 1;26(2):284-285. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.015. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 28768166
References
-
- Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP. A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:185–193. - PubMed
-
- Brix G, Zaers J, Adam LE, Bellemann ME, Ostertag H, Trojan H, Haberkorn U, Doll J, Oberdorfer F, Lorenz WJ. Performance evaluation of a whole-body PET scanner using the NEMA protocol. National Electrical Manufacturers Association. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine. 1997;38:1614–1623. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 NS006833/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 NS057901/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS048056/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UF1 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG032438/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P20 MH077967/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005681/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB009352/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS098577/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

