Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Inhibition Reduces Hepatic Steatosis but Elevates Plasma Triglycerides in Mice and Humans: A Bedside to Bench Investigation
- PMID: 28768177
- PMCID: PMC5603267
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.07.009
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Inhibition Reduces Hepatic Steatosis but Elevates Plasma Triglycerides in Mice and Humans: A Bedside to Bench Investigation
Erratum in
-
Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Inhibition Reduces Hepatic Steatosis but Elevates Plasma Triglycerides in Mice and Humans: A Bedside to Bench Investigation.Cell Metab. 2017 Sep 5;26(3):576. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.08.011. Cell Metab. 2017. PMID: 28877461 No abstract available.
Abstract
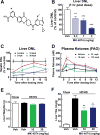
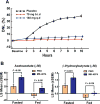
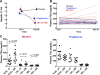
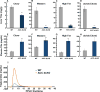
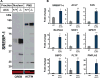
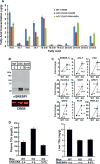
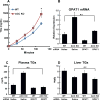
Inhibiting lipogenesis prevents hepatic steatosis in rodents with insulin resistance. To determine if reducing lipogenesis functions similarly in humans, we developed MK-4074, a liver-specific inhibitor of acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC1) and (ACC2), enzymes that produce malonyl-CoA for fatty acid synthesis. MK-4074 administered to subjects with hepatic steatosis for 1 month lowered lipogenesis, increased ketones, and reduced liver triglycerides by 36%. Unexpectedly, MK-4074 increased plasma triglycerides by 200%. To further investigate, mice that lack ACC1 and ACC2 in hepatocytes (ACC dLKO) were generated. Deletion of ACCs decreased polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) concentrations in liver due to reduced malonyl-CoA, which is required for elongation of essential fatty acids. PUFA deficiency induced SREBP-1c, which increased GPAT1 expression and VLDL secretion. PUFA supplementation or siRNA-mediated knockdown of GPAT1 normalized plasma triglycerides. Thus, inhibiting lipogenesis in humans reduced hepatic steatosis, but inhibiting ACC resulted in hypertriglyceridemia due to activation of SREBP-1c and increased VLDL secretion.
Keywords: SREBPs; acetyl-CoA carboxylase; hepatic steatosis; hypertriglyceridemia; inhibitors; lipogenesis; malonyl-CoA.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aarsland A, Chinkes D, Wolfe RR. Hepatic and whole-body fat synthesis in humans during carbohydrate overfeeding. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997;65:1774–1782. - PubMed
-
- Abu-Elheiga L, Matzuk MM, Abo-Hashema KAH, Wakil SJ. Continuous fatty acid oxidation and reduced fat storage in mice lacking acetyl-CoA carboxylase 2. Science. 2001;291:2613–2616. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

