Speech Understanding in Noise by Patients With Cochlear Implants Using a Monaural Adaptive Beamformer
- PMID: 28768324
- PMCID: PMC5829808
- DOI: 10.1044/2017_JSLHR-H-16-0312
Speech Understanding in Noise by Patients With Cochlear Implants Using a Monaural Adaptive Beamformer
Abstract
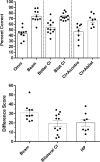
Purpose: The aim of this experiment was to compare, for patients with cochlear implants (CIs), the improvement for speech understanding in noise provided by a monaural adaptive beamformer and for two interventions that produced bilateral input (i.e., bilateral CIs and hearing preservation [HP] surgery).
Method: Speech understanding scores for sentences were obtained for 10 listeners fit with a single CI. The listeners were tested with and without beamformer activated in a "cocktail party" environment with spatially separated target and maskers. Data for 10 listeners with bilateral CIs and 8 listeners with HP CIs were taken from Loiselle, Dorman, Yost, Cook, and Gifford (2016), who used the same test protocol.
Results: The use of the beamformer resulted in a 31 percentage point improvement in performance; in bilateral CIs, an 18 percentage point improvement; and in HP CIs, a 20 percentage point improvement.
Conclusion: A monaural adaptive beamformer can produce an improvement in speech understanding in a complex noise environment that is equal to, or greater than, the improvement produced by bilateral CIs and HP surgery.
Figures

References
-
- Bichey B., & Miyamoto R. (2008). Outcomes in bilateral cochlear implantation. Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery, 138, 655–661. - PubMed
-
- Compton-Conley C., Neuman A., Killion M., & Levitt H. (2004). Performance of directional microphones for hearing aids: Real world versus simulation. Journal of the American Academy of Audiology, 15, 440–455. - PubMed
-
- Elko G., & Pong A.-T. N. (1995). A simple adaptive first-order differential microphone. Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (pp. 169–171). New Paltz, NY: IEEE.
-
- Hehrmann P., Fredelake S., Hamacher V., Dyballa K.-H., & Buchner A. (2012). Improved speech intelligibility with cochlear implants using state of the art noise reduction algorithms. Proceedings of the ITG Symposium on Speech Communication, 10, 1–3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

