New Insights into 5hmC DNA Modification: Generation, Distribution and Function
- PMID: 28769976
- PMCID: PMC5515870
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00100
New Insights into 5hmC DNA Modification: Generation, Distribution and Function
Abstract
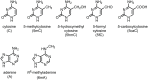
Dynamic DNA modifications, such as methylation/demethylation on cytosine, are major epigenetic mechanisms to modulate gene expression in both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In addition to the common methylation on the 5th position of the pyrimidine ring of cytosine (5mC), other types of modifications at the same position, such as 5-hydroxymethyl (5hmC), 5-formyl (5fC), and 5-carboxyl (5caC), are also important. Recently, 5hmC, a product of 5mC demethylation by the Ten-Eleven Translocation family proteins, was shown to regulate many cellular and developmental processes, including the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells, neuron development, and tumorigenesis in mammals. Here, we review recent advances on the generation, distribution, and function of 5hmC modification in mammals and discuss its potential roles in plants.
Keywords: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine; DNA demethylation; DNA hydroxylation; TET proteins; epigenetics.
Figures

References
-
- Almeida R. D., Sottile V., Loose M., De Sousa P. A., Johnson A. D., Ruzov A. (2012). Semi-quantitative immunohistochemical detection of 5-hydroxymethyl-cytosine reveals conservation of its tissue distribution between amphibians and mammals. Epigenetics 7 137–140. 10.4161/epi.7.2.18949 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

