Complete genome sequence of a commensal bacterium, Hafnia alvei CBA7124, isolated from human feces
- PMID: 28770009
- PMCID: PMC5530468
- DOI: 10.1186/s13099-017-0190-0
Complete genome sequence of a commensal bacterium, Hafnia alvei CBA7124, isolated from human feces
Abstract
Background: Members of the genus Hafnia have been isolated from the feces of mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish, as well as from soil, water, sewage, and foods. Hafnia alvei is an opportunistic pathogen that has been implicated in intestinal and extraintestinal infections in humans. However, its pathogenicity is still unclear. In this study, we isolated H. alvei from human feces and performed sequencing as well as comparative genomic analysis to better understand its pathogenicity.
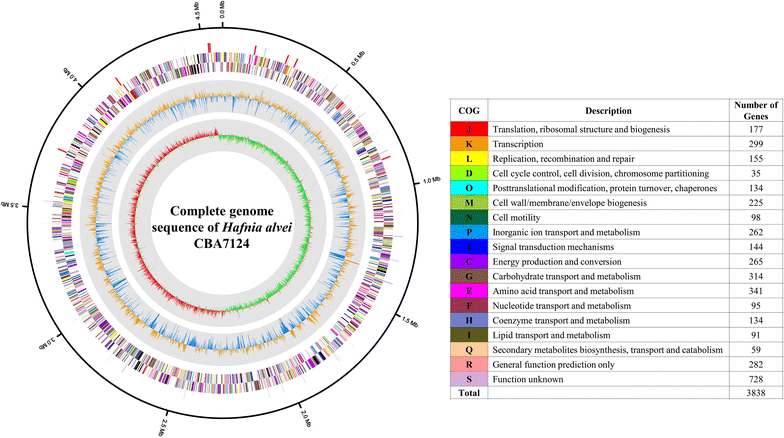
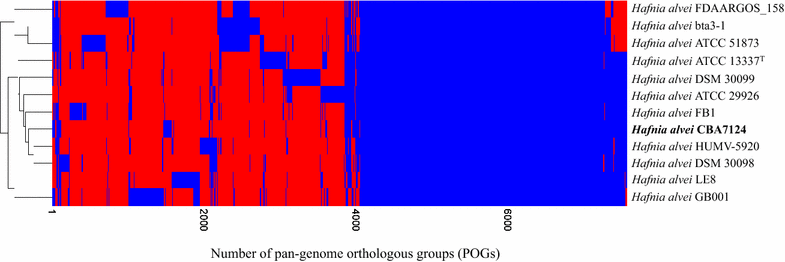
Results: The genome of H. alvei CBA7124 comprised a single circular chromosome with 4,585,298 bp and a GC content of 48.8%. The genome contained 25 rRNA genes (9 5S rRNA genes, 8 16S rRNA genes, and 8 23S rRNA genes), 88 tRNA genes, and 4043 protein-coding genes. Using comparative genomic analysis, the genome of this strain was found to have 72 strain-specific singletons. The genome also contained genes for antibiotic and antimicrobial resistance, as well as toxin-antitoxin systems.
Conclusions: We revealed the complete genome sequence of the opportunistic gut pathogen, H. alvei CBA7124. We also performed comparative genomic analysis of the sequences in the genome of H. alvei CBA7124, and found that it contained strain-specific singletons, antibiotic resistance genes, and toxin-antitoxin systems. These results could improve our understanding of the pathogenicity and the mechanism behind the antibiotic resistance of H. alvei strains.
Keywords: Comparative genomics; Complete genome sequence; Gut microbiota; Hafnia alvei CBA7124.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative genomic analysis of the Hafnia genus reveals an explicit evolutionary relationship between the species alvei and paralvei and provides insights into pathogenicity.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 23;20(1):768. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6123-1. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31646960 Free PMC article.
-
The complete genome sequence of Hafnia alvei A23BA; a potential antibiotic-producing rhizobacterium.BMC Res Notes. 2021 Jan 6;14(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-05418-2. BMC Res Notes. 2021. PMID: 33407900 Free PMC article.
-
Specific Strains of Honeybee Gut Lactobacillus Stimulate Host Immune System to Protect against Pathogenic Hafnia alvei.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0189621. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01896-21. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 34985299 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiology of Hafnia alvei.Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020 Jan;38 Suppl 1:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2020.02.001. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 32111359 Review. English, Spanish.
-
The genus Hafnia: from soup to nuts.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;19(1):12-8. doi: 10.1128/CMR.19.1.12-28.2006. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16418520 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of feeding on different parts of Ailanthus altissima on the intestinal microbiota of Eucryptorrhynchus scrobiculatus and Eucryptorrhynchus brandti (Coleoptera: Curculionidae).Front Microbiol. 2022 Aug 4;13:899313. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.899313. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35992686 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting host identification of bacteriophage Enc34: from biochemical to molecular.J Virol. 2024 Mar 19;98(3):e0173123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01731-23. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38329345 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of the Hafnia genus reveals an explicit evolutionary relationship between the species alvei and paralvei and provides insights into pathogenicity.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 23;20(1):768. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6123-1. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31646960 Free PMC article.
-
Host genetic background rather than diet-induced gut microbiota shifts of sympatric black-necked crane, common crane and bar-headed goose.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 12;14:1270716. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1270716. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37933251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McBee ME, Schauer DB. The genus Hafnia. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E, editors. The Prokaryotes. New York: Springer; 2006. pp. 215–8.
-
- Viana ES, Campos ME, Ponce AR, Mantovani HC, Vanetti MC. Biofilm formation and acyl homoserine lactone production in Hafnia alvei isolated from raw milk. Biol Res. 2009;42:427–436. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

