Ocular Adverse Effects of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Are Potentiated by Intermittent Hypoxia in a Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy
- PMID: 28770109
- PMCID: PMC5523466
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4353129
Ocular Adverse Effects of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Are Potentiated by Intermittent Hypoxia in a Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy
Abstract
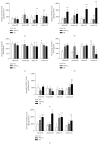
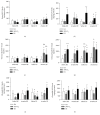
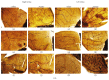
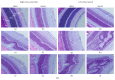
Intravitreal bevacizumab (Avastin) use in preterm infants with retinopathy of prematurity is associated with severe neurological disabilities, suggesting vascular leakage. We examined the hypothesis that intermittent hypoxia (IH) potentiates intravitreal Avastin leakage. Neonatal rats at birth were exposed to IH from birth (P0)-P14. At P14, the time of eye opening in rats, a single dose of Avastin (0.125 mg) was injected intravitreally into the left eye. Animals were placed in room air (RA) until P23 or P45 for recovery (IHR). Hyperoxia-exposed and RA littermates served as oxygen controls, and equivalent volume saline served as the placebo controls. At P23 and P45 ocular angiogenesis, retinal pathology and ocular and systemic biomarkers of angiogenesis were examined. Retinal flatmounts showed poor peripheral vascularization in Avastin-treated and fellow eyes at P23, with numerous punctate hemorrhages and dilated, tortuous vessels with anastomoses at P45 in the rats exposed to IH. These adverse effects were associated with robust increases in systemic VEGF and in both treated and untreated fellow eyes. Histological analysis showed severe damage in the inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers. Exposure of IH/IHR-induced injured retinal microvasculature to anti-VEGF substances can result in vascular leakage and adverse effects in the developing neonate.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acute and chronic effects of intravitreal bevacizumab on lung biomarkers of angiogenesis in the rat exposed to neonatal intermittent hypoxia.Exp Lung Res. 2021 Apr;47(3):121-135. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2020.1866712. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Exp Lung Res. 2021. PMID: 33377400
-
Intravitreal bevacizumab alters type IV collagenases and exacerbates arrested alveologenesis in the neonatal rat lungs.Exp Lung Res. 2017 Apr;43(3):120-133. doi: 10.1080/01902148.2017.1306897. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Exp Lung Res. 2017. PMID: 28409646
-
Impact of Chronic Neonatal Intermittent Hypoxia on Severity of Retinal Damage in a Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy.J Nat Sci. 2018;4(3):e488. J Nat Sci. 2018. PMID: 29552637 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen peroxide accumulation in the choroid during intermittent hypoxia increases risk of severe oxygen-induced retinopathy in neonatal rats.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Nov 19;54(12):7644-57. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13040. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 24168990 Free PMC article.
-
[Off-label use of intravitreal bevacizumab for severe retinopathy of prematurity].Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015 Feb;90(2):81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.oftal.2014.09.011. Epub 2014 Nov 15. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 25459682 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy from Recurrent Intermittent Hypoxia Is Not Dependent on Resolution with Room Air or Oxygen, in Neonatal Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 1;19(5):1337. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051337. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29724000 Free PMC article.
-
Ocular Versus Oral Propranolol for Prevention and/or Treatment of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy in a Rat Model.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Mar;37(2):112-130. doi: 10.1089/jop.2020.0092. Epub 2021 Feb 3. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33535016 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Bevacizumab and Aflibercept for Suppression of Angiogenesis in Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Jun 29;16(7):939. doi: 10.3390/ph16070939. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37513851 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Effects of Coenzyme Q10 or n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Supplementation on Retinal Angiogenesis in a Rat Model of Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2018 Nov 9;7(11):160. doi: 10.3390/antiox7110160. Antioxidants (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30423931 Free PMC article.
-
Response of Pediatric Choroidal Neovascularization to Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.Cureus. 2021 Dec 6;13(12):e20195. doi: 10.7759/cureus.20195. eCollection 2021 Dec. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 35004017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chow L. C., Wright K. W., Sola A., CSMC Oxygen Administration Study Group Can changes in clinical practice decrease the incidence of severe retinopathy of prematurity in very low birth weight infants? Pediatrics. 2003;111:339–345. - PubMed
-
- Gergely K., Gerinec A. Retinopathy of prematurity-epidemics, incidence, prevalence, blindness. Bratislavské Lekárske Listy. 2010;111:514–517. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

