Respiratory infections are temporally associated with initiation of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity: the TEDDY study
- PMID: 28770319
- PMCID: PMC5697762
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-017-4365-5
Respiratory infections are temporally associated with initiation of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity: the TEDDY study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Respiratory infections are temporally associated with initiation of type 1 diabetes autoimmunity: the TEDDY study.Diabetologia. 2018 Jan;61(1):254. doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4487-9. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29080005
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Respiratory infections and onset of islet autoimmunity are reported to correlate positively in two small prospective studies. The Environmental Determinants of Diabetes in the Young (TEDDY) study is the largest prospective international cohort study on the environmental determinants of type 1 diabetes that regularly monitors both clinical infections and islet autoantibodies. The aim was to confirm the influence of reported respiratory infections and to further characterise the temporal relationship with autoantibody seroconversion.
Methods: During the years 2004-2009, 8676 newborn babies with HLA genotypes conferring an increased risk of type 1 diabetes were enrolled at 3 months of age to participate in a 15 year follow-up. In the present study, the association between parent-reported respiratory infections and islet autoantibodies at 3 month intervals up to 4 years of age was evaluated in 7869 children. Time-dependent proportional hazard models were used to assess how the timing of respiratory infections related to persistent confirmed islet autoimmunity, defined as autoantibody positivity against insulin, GAD and/or insulinoma antigen-2, concordant at two reference laboratories on two or more consecutive visits.
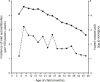
Results: In total, 87,327 parent-reported respiratory infectious episodes were recorded while the children were under study surveillance for islet autoimmunity, and 454 children seroconverted. The number of respiratory infections occurring in a 9 month period was associated with the subsequent risk of autoimmunity (p < 0.001). For each 1/year rate increase in infections, the hazard of islet autoimmunity increased by 5.6% (95% CI 2.5%, 8.8%). The risk association was linked primarily to infections occurring in the winter (HR 1.42 [95% CI 1.16, 1.74]; p < 0.001). The types of respiratory infection independently associated with autoimmunity were common cold, influenza-like illness, sinusitis, and laryngitis/tracheitis, with HRs (95% CI) of 1.38 (1.11, 1.71), 2.37 (1.35, 4.15), 2.63 (1.22, 5.67) and 1.76 (1.04, 2.98), respectively.
Conclusions/interpretation: Recent respiratory infections in young children correlate with an increased risk of islet autoimmunity in the TEDDY study. Further studies to identify the potential causative viruses with pathogen-specific assays should focus especially on the 9 month time window leading to autoantibody seroconversion.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Islet autoantibodies; Prospective cohort; Respiratory infections; Type 1 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Rasmussen T, Witsø E, Tapia G, Stene LC, Rønningen KS. Self-reported lower respiratory tract infections and development of islet autoimmunity in children with the type 1 diabetes high-risk HLA genotype: the MIDIA study. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2011;27:834–837. - PubMed
-
- Beyerlein A, Wehweck F, Ziegler AG, Pflueger M. Respiratory infections in early life and the development of islet autoimmunity in children at increased type 1 diabetes risk evidence from the BABYDIET Study. JAMA Pediatr. 2013;167:800–807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN267200700014C/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063790/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000064/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK095300/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063861/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063829/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063821/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063836/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK112243/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK063865/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK063863/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106955/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK100238/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

