Activity of a novel protonophore against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 28771026
- PMCID: PMC5941710
- DOI: 10.4155/fmc-2017-0047
Activity of a novel protonophore against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Aim: Compound 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4,4-trifluoro-3-hydroxy-2-buten-1-one (compound 1) was identified as a hit against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain MW2.
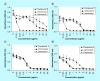
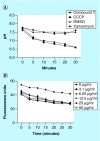
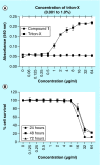
Methods & results: The MIC of compound 1 against MRSA was 4 μg/ml. The compound showed enhanced activity at acidic pH by lowering bacterial intracellular pH and exhibited no lysis of human red blood cells at up to 64 μg/ml and its IC50 against HepG2 cells was 32 μg/ml. The compound reduced 1-log10 colony forming units of intracellular MRSA in macrophages and prolonged the survival of MRSA-infected Caenorhabditis elegans (p = 0.0015) and Galleria mellonella (p = 0.0002).
Conclusion: Compound 1 is a protonophore with potent in vitro and in vivo activity against MRSA and no toxicity in mammalian cells up to 8 μg/ml that warrants further investigation as a novel antibacterial.
Keywords: Galleria mellonella; MRSA infection; S. aureus; antibiotic; macrophages; protonophore.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was supported by NIH grant P01 AI083214 to E Mylonakis. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Anti-MRSA agent discovery using Caenorhabditis elegans-based high-throughput screening.J Microbiol. 2020 Jun;58(6):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0163-8. Epub 2020 May 27. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32462486 Review.
-
Antibacterial Properties of Four Novel Hit Compounds from a Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus-Caenorhabditis elegans High-Throughput Screen.Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Jun;24(5):666-674. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2017.0250. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29461939 Free PMC article.
-
Arylthiazole antibiotics targeting intracellular methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) that interfere with bacterial cell wall synthesis.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Oct 20;139:665-673. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.039. Epub 2017 Aug 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28846967 Free PMC article.
-
The Neutrally Charged Diarylurea Compound PQ401 Kills Antibiotic-Resistant and Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus.mBio. 2020 Jun 30;11(3):e01140-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01140-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32605985 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and antibacterial evaluation of a novel series of synthetic phenylthiazole compounds against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Apr 13;94:306-16. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Mar 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25771109 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Repurposing the anthelmintic drug niclosamide to combat Helicobacter pylori.Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 27;8(1):3701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22037-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29487357 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of new carbonyl cyanide aromatic hydrazones on biofilm inhibition against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.RSC Adv. 2020 May 7;10(30):17854-17861. doi: 10.1039/d0ra03124k. eCollection 2020 May 5. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35515581 Free PMC article.
-
New solvent options for in vivo assays in the Galleria mellonella larvae model.Virulence. 2019 Dec;10(1):776-782. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2019.1659663. Virulence. 2019. PMID: 31451073 Free PMC article.
-
The Anti-virulence Efficacy of 4-(1,3-Dimethyl-2,3-Dihydro-1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)Phenol Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jul 17;10:1557. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01557. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31379761 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-MRSA agent discovery using Caenorhabditis elegans-based high-throughput screening.J Microbiol. 2020 Jun;58(6):431-444. doi: 10.1007/s12275-020-0163-8. Epub 2020 May 27. J Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32462486 Review.
References
-
- Wertheim HF, Melles DC, Vos MC, et al. The role of nasal carriage in Staphylococcus aureus infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2005;5(12):751–762. - PubMed
-
- Mulligan ME, Murray-Leisure KA, Ribner BS, et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a consensus review of the microbiology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology with implications for prevention and management. Am. J. Med. 1993;94(3):313–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
