Somatic Host Cell Alterations in HPV Carcinogenesis
- PMID: 28771191
- PMCID: PMC5580463
- DOI: 10.3390/v9080206
Somatic Host Cell Alterations in HPV Carcinogenesis
Abstract
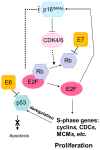
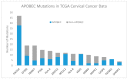
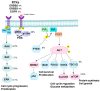
High-risk human papilloma virus (HPV) infections cause cancers in different organ sites, most commonly cervical and head and neck cancers. While carcinogenesis is initiated by two viral oncoproteins, E6 and E7, increasing evidence shows the importance of specific somatic events in host cells for malignant transformation. HPV-driven cancers share characteristic somatic changes, including apolipoprotein B mRNA editing catalytic polypeptide-like (APOBEC)-driven mutations and genomic instability leading to copy number variations and large chromosomal rearrangements. HPV-associated cancers have recurrent somatic mutations in phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) and phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), human leukocyte antigen A and B (HLA-A and HLA-B)-A/B, and the transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) pathway, and rarely have mutations in the tumor protein p53 (TP53) and RB transcriptional corepressor 1 (RB1) tumor suppressor genes. There are some variations by tumor site, such as NOTCH1 mutations which are primarily found in head and neck cancers. Understanding the somatic events following HPV infection and persistence can aid the development of early detection biomarkers, particularly when mutations in precancers are characterized. Somatic mutations may also influence prognosis and treatment decisions.
Keywords: APOBEC; HPV; cervical cancer; chromosomal instability; copy number variation; head and neck cancer; integration; significantly mutated gene; somatic mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
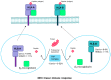
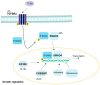
References
-
- Walboomers J.M., Jacobs M.V., Manos M.M., Bosch F.X., Kummer J.A., Shah K.V., Snijders P.J., Peto J., Meijer C.J., Munoz N. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J. Pathol. 1999;189:12–19. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9896(199909)189:1<12::AID-PATH431>3.0.CO;2-F. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ndiaye C., Mena M., Alemany L., Arbyn M., Castellsague X., Laporte L., Bosch F.X., de Sanjose S., Trottier H. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4A detection in head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:1319–1331. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70471-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hartwig S., Baldauf J.-J., Dominiak-Felden G., Simondon F., Alemany L., de Sanjosé S., Castellsagué X. Estimation of the epidemiological burden of HPV-related anogenital cancers, precancerous lesions, and genital warts in women and men in europe: Potential additional benefit of a nine-valent second generation HPV vaccine compared to first generation HPV vaccines. Papillomavirus Res. 2015;1:90–100.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

