The Fetus Can Teach Us: Oxygen and the Pulmonary Vasculature
- PMID: 28771211
- PMCID: PMC5575589
- DOI: 10.3390/children4080067
The Fetus Can Teach Us: Oxygen and the Pulmonary Vasculature
Abstract
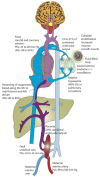
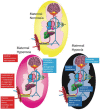
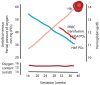
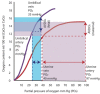
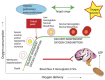
Neonates suffering from pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN) continue to represent an important proportion of patients requiring intensive neonatal care, and have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality. The human fetus has evolved to maintain a high pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) in utero to allow the majority of the fetal circulation to bypass the lungs, which do not participate in gas exchange, towards the low resistance placenta. At birth, oxygen plays a major role in decreasing PVR to enhance pulmonary blood flow and establish the lungs as the organ of gas exchange. The failure of PVR to fall following birth results in PPHN, and oxygen remains the mainstay therapeutic intervention in the management of PPHN. Knowledge gaps on what constitutes the optimal oxygenation target leads to a wide variation in practices, and often leads to excessive oxygen use. Owing to the risk of oxygen toxicity, avoiding hyperoxemia is as important as avoiding hypoxemia in the management of PPHN. Current evidence supports maintaining arterial oxygen tension in the range of 50-80 mm Hg, and oxygen saturation between 90-97% in term infants with hypoxemic respiratory failure. Clinical studies evaluating the optimal oxygenation in the treatment of PPHN will be enthusiastically awaited.
Keywords: fetal circulation; oxygen saturation; oxygen target; pulmonary hypertension of the newborn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in the Newborn.Children (Basel). 2017 Jul 28;4(8):63. doi: 10.3390/children4080063. Children (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28788074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Do We Monitor Oxygenation during the Management of PPHN? Alveolar, Arterial, Mixed Venous Oxygen Tension or Peripheral Saturation?Children (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;7(10):180. doi: 10.3390/children7100180. Children (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066076 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Considerations in the management of hypoxemic respiratory failure and persistent pulmonary hypertension in term and late preterm neonates.J Perinatol. 2016 Jun;36 Suppl 2:S12-9. doi: 10.1038/jp.2016.44. J Perinatol. 2016. PMID: 27225960 Review.
-
Optimal oxygenation and role of free radicals in PPHN.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Oct;142:97-106. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 Apr 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30995536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fetal circulation, pathophysiology of hypoxemic respiratory failure and pulmonary hypertension in neonates, and the role of oxygen therapy.J Perinatol. 2016 Jun;36 Suppl 2:S3-S11. doi: 10.1038/jp.2016.43. J Perinatol. 2016. PMID: 27225963 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhaled Nitric Oxide at Birth Reduces Pulmonary Vascular Resistance and Improves Oxygenation in Preterm Lambs.Children (Basel). 2021 May 11;8(5):378. doi: 10.3390/children8050378. Children (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34064629 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-210 Mediates Hypoxic Pulmonary Hypertension in the Newborn Lamb.Hypertension. 2025 Jun;82(6):1151-1163. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.23061. Epub 2025 Apr 23. Hypertension. 2025. PMID: 40265266
-
The CoDiNOS trial protocol: an international randomised controlled trial of intravenous sildenafil versus inhaled nitric oxide for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia.BMJ Open. 2019 Nov 5;9(11):e032122. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032122. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31694851 Free PMC article.
-
Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) Co-Culture with Osteogenic Cells: From Molecular Communication to Engineering Prevascularised Bone Grafts.J Clin Med. 2019 Oct 3;8(10):1602. doi: 10.3390/jcm8101602. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31623330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Pulmonary Hypertension in Preterm Infants.Clin Perinatol. 2024 Mar;51(1):171-193. doi: 10.1016/j.clp.2023.11.005. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Clin Perinatol. 2024. PMID: 38325940 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gersony W., Duc G., Sinclair J. “Pfc syndrome” (persistence of the fetal circulation) Circulation. 1969:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Aschner J.L., Gien J., Ambalavanan N., Kinsella J.P., Konduri G.G., Lakshminrusimha S., Saugstad O.D., Steinhorn R.H. Challenges, priorities and novel therapies for hypoxemic respiratory failure and pulmonary hypertension in the neonate. J. Perinatol. 2016;36:S32–S36. doi: 10.1038/jp.2016.47. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

