FGFR1 is critical for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline via induction of the MAP4K4 pathway
- PMID: 28771231
- PMCID: PMC5596544
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2017.353
FGFR1 is critical for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline via induction of the MAP4K4 pathway
Abstract
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) has been shown to contribute to organ fibrogenesis, and we have reported that the anti-EndMT effect of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (AcSDKP) is associated with restoring expression of diabetes-suppressed fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR), the key anti-EndMT molecule. FGFR1 is the key inhibitor of EndMT via the suppression of the transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) signaling pathway, and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP4K4) inhibits integrin β1, a key factor in activating TGFβ signaling and EndMT. Here, we showed that the close proximity between AcSDKP and FGFR1 was essential for the suppression of TGFβ/smad signaling and EndMT associated with MAP4K4 phosphorylation (P-MAP4K4) in endothelial cells. In cultured human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs), the anti-EndMT and anti-TGFβ/smad effects of AcSDKP were lost following treatment with a neutralizing FGFR1 antibody (N-FGFR1) or transfection of FRS2 siRNA. The physical interaction between FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 in HMVECs was confirmed by proximity ligation analysis and an immunoprecipitation assay. AcSDKP induced P-MAP4K4 in HMVECs, which was significantly inhibited by treatment with either N-FGFR1 or FRS2 siRNA. Furthermore, MAP4K4 knockdown using specific siRNAs induced smad3 phosphorylation and EndMT in HMVECs, which was not suppressed by AcSDKP. Streptozotocin-induced diabetic CD-1 mice exhibited suppression of both FGFR1 and P-MAP4K4 expression levels associated with the induction of TGFβ/smad3 signaling and EndMT in their hearts and kidneys; those were restored by AcSDKP treatment. These data demonstrate that the AcSDKP-FGFR1-MAP4K4 axis has an important role in combating EndMT-associated fibrotic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
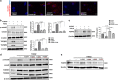






Similar articles
-
βklotho is essential for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effects of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 May;9(5):1029-1038. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12638. Epub 2019 Apr 22. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 30972974 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial FGFR1 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1) Deficiency Contributes Differential Fibrogenic Effects in Kidney and Heart of Diabetic Mice.Hypertension. 2020 Dec;76(6):1935-1944. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15587. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 33131311
-
FGFR1 is essential for N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by upregulating microRNA let-7b-5p.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Jan 15;495(3):2214-2220. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.089. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29269295
-
microRNA Crosstalk Influences Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal, Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal, and Macrophage-to-Mesenchymal Transitions in the Kidney.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 16;10:904. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00904. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31474862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline is a valuable endogenous antifibrotic peptide for kidney fibrosis in diabetes: An update and translational aspects.J Diabetes Investig. 2020 May;11(3):516-526. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13219. Epub 2020 Mar 11. J Diabetes Investig. 2020. PMID: 31997585 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
lncRNA MALAT1 Promotes Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy by Targeting the miR-2355-3p/IL6ST Axis.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 29;12:647650. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.647650. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33995063 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition: Role in Physiology and in the Pathogenesis of Human Diseases.Physiol Rev. 2019 Apr 1;99(2):1281-1324. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 30864875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic modification in diabetic kidney disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 30;14:1133970. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1133970. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
βklotho is essential for the anti-endothelial mesenchymal transition effects of N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline.FEBS Open Bio. 2019 May;9(5):1029-1038. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12638. Epub 2019 Apr 22. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 30972974 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of PGP 9.5, NGFR, TGFβ1, FGFR1, MMP-2, AT2R2, SHH, and TUNEL in Primary Obstructive Megaureter Tissue.J Histochem Cytochem. 2022 Feb;70(2):139-149. doi: 10.1369/00221554211063515. Epub 2021 Dec 17. J Histochem Cytochem. 2022. PMID: 34915763 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He J, Xu Y, Koya D, Kanasaki K. Role of the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in renal fibrosis of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 2013; 17: 488–497. - PubMed
-
- Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M, Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med 2007; 13: 952–961. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

