Comprehensive analysis of nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of mRNA in Drosophila cells
- PMID: 28771467
- PMCID: PMC5557608
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006929
Comprehensive analysis of nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of mRNA in Drosophila cells
Abstract
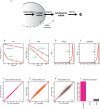
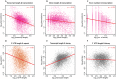
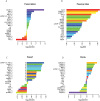
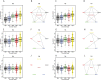
Eukaryotic mRNAs undergo a cycle of transcription, nuclear export, and degradation. A major challenge is to obtain a global, quantitative view of these processes. Here we measured the genome-wide nucleocytoplasmic dynamics of mRNA in Drosophila cells by metabolic labeling in combination with cellular fractionation. By mathematical modeling of these data we determined rates of transcription, export and cytoplasmic decay for 5420 genes. We characterized these kinetic rates and investigated links with mRNA features, RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) and chromatin states. We found prominent correlations between mRNA decay rate and transcript size, while nuclear export rates are linked to the size of the 3'UTR. Transcription, export and decay rates are each associated with distinct spectra of RBPs. Specific classes of genes, such as those encoding cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins, exhibit characteristic combinations of rate constants, suggesting modular control. Binding of splicing factors is associated with faster rates of export, and our data suggest coordinated regulation of nuclear export of specific functional classes of genes. Finally, correlations between rate constants suggest global coordination between the three processes. Our approach provides insights into the genome-wide nucleocytoplasmic kinetics of mRNA and should be generally applicable to other cell systems.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Dolken L., et al. High-resolution gene expression profiling for simultaneous kinetic parameter analysis of RNA synthesis and decay. RNA, 2008. 14(9): p. 1959–72. doi: 10.1261/rna.1136108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rabani M., et al. Metabolic labeling of RNA uncovers principles of RNA production and degradation dynamics in mammalian cells. Nat Biotechnol, 2011. 29(5): p. 436–42. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1861 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhatt D.M., et al. Transcript dynamics of proinflammatory genes revealed by sequence analysis of subcellular RNA fractions. Cell, 2012. 150(2): p. 279–90. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.043 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eser P., et al. Periodic mRNA synthesis and degradation co-operate during cell cycle gene expression. Mol Syst Biol, 2014. 10: p. 717 doi: 10.1002/msb.134886 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

