Production of an anti-Aβ antibody fragment in Pichia pastoris and in vitro and in vivo validation of its therapeutic effect
- PMID: 28771492
- PMCID: PMC5542431
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181480
Production of an anti-Aβ antibody fragment in Pichia pastoris and in vitro and in vivo validation of its therapeutic effect
Abstract
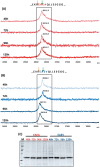
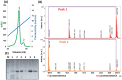
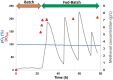
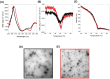
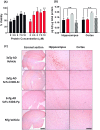
ScFv-h3D6 has been shown as an efficient therapy in the 3xTg-AD mouse model of Alzheimer's Disease. Because one of the major bottlenecks for the therapeutic uses of proteins produced in Escherichia coli is their potential contamination with endotoxins, LPS were extensively removed by a rather low-efficient, expensive, and time-consuming purification step. In addition, disulfide scrambling is favored in the reducing bacterial cytoplasm albeit the use of reductase deficient strains. To overcome these hurdles, as well as to improve the yield, the yeast Pichia pastoris, an endotoxin-free host system for recombinant protein production, has been used to produce scFv-h3D6, both in flask and in a fed-batch bioreactor. Comparison of the thermal stability of the obtained protein with that from E. coli showed no differences. Opposite to the case of the protein obtained from E. coli, no disulfide scrambled conformations or LPS traces were detected in that produced in P. pastoris. Cytotoxicity assays in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cell-cultures demonstrated that proteins from both expression systems were similarly efficient in precluding Aβ-induced toxicity. Finally, the 3xTg-AD mouse model was used to test the therapeutic effect of both proteins. Quantification of Aβ levels from cortex and hippocampus protein extracts by ELISA, and Aβ-immunohistochemistry, showed that both proteins reduced Aβ burden. This work demonstrates that scFv-h3D6 obtained from P. pastoris shows the same benefits as those already known for that obtained from E. coli, with multiple advantages in terms of recombinant production and safety.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Waldmann TA. Immunotherapy: past, present and future. Nat Med. 2003;9:269–77. doi: 10.1038/nm0303-269 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002;297:353–6. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hardy J. Alzheimer’s disease: the amyloid cascade hypothesis: an update and reappraisal. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9 3 Suppl:151–3. - PubMed
-
- Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ. A beta oligomers—a decade of discovery. J Neurochem. 2007;101:1172–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.04426.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tomic JL, Pensalfini A, Head E, Glabe CG. Soluble fibrillar oligomer levels are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease brain and correlate with cognitive dysfunction. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;35:352–8. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.05.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

