Quantitative proteomics in A30P*A53T α-synuclein transgenic mice reveals upregulation of Sel1l
- PMID: 28771510
- PMCID: PMC5542467
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0182092
Quantitative proteomics in A30P*A53T α-synuclein transgenic mice reveals upregulation of Sel1l
Abstract
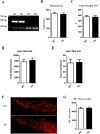
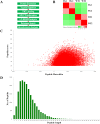
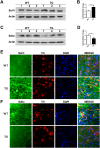
α-Synuclein is an abundantly expressed neuronal protein that is at the center of focus in understanding a group of neurodegenerative disorders called synucleinopathies, which are characterized by the intracellular presence of aggregated α-synuclein. However, the mechanism of α-synuclein biology in synucleinopathies pathogenesis is not fully understood. In this study, mice overexpressing human A30P*A53T α-synuclein were evaluated by a motor behavior test and count of TH-positive neurons, and then two-dimensional liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry coupled with tandem mass tags (TMTs) labeling was employed to quantitatively identify the differentially expressed proteins of substantia nigra pars compacta (SNpc) tissue samples that were obtained from the α-synuclein transgenic mice and wild type controls. The number of SNpc dopaminergic neurons and the motor behavior were unchanged in A30P*A53T transgenic mice at the age of 6 months. Of the 4,715 proteins identified by proteomic techniques, 271 were differentially expressed, including 249 upregulated and 22 downregulated proteins. These alterations were primarily associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, ubiquitin-proteasome system impairment, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. Some obviously changed proteins, which were validated by western blotting and immunofluorescence staining, including Sel1l and Sdhc, may be involved in the α-synuclein pathologies of synucleinopathies. A biological pathway analysis of common related proteins showed that the proteins were linked to a total of 31 KEGG pathways. Our findings suggest that these identified proteins may serve as novel therapeutic targets for synucleinopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Kim WS, Kagedal K, Halliday GM. Alpha-synuclein biology in Lewy body diseases. Alzheimer's research & therapy. 2014;6(5):73 doi: 10.1186/s13195-014-0073-2 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Burre J, Sharma M, Sudhof TC. Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of alpha-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine. 2017. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a024091 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chung CY, Khurana V, Yi S, Sahni N, Loh KH, Auluck PK, et al. In Situ Peroxidase Labeling and Mass-Spectrometry Connects Alpha-Synuclein Directly to Endocytic Trafficking and mRNA Metabolism in Neurons. Cell systems. 2017. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.01.002 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ingelsson M. Alpha-Synuclein Oligomers-Neurotoxic Molecules in Parkinson's Disease and Other Lewy Body Disorders. Frontiers in neuroscience. 2016;10:408 doi: 10.3389/fnins.2016.00408 ; - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dehay B, Fernagut PO. Alpha-synuclein-based models of Parkinson's disease. Revue neurologique. 2016;172(6–7):371–8. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2016.04.003 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

