The neuroprotective agent Rasagiline mesylate attenuates cardiac remodeling after experimental myocardial infarction
- PMID: 28772050
- PMCID: PMC5542732
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.12140
The neuroprotective agent Rasagiline mesylate attenuates cardiac remodeling after experimental myocardial infarction
Abstract
Aim: Rasagiline mesylate (N-propargyl-1 (R)-aminoindan) (RG) is a selective, potent irreversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase-B with cardioprotective and anti-apoptotic properties. We investigated whether it could be cardioprotective in a rat model undergoing experimental myocardial infarction (MI) by permanent ligation of the left anterior descending coronary artery.
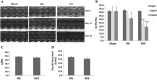
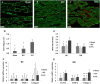
Methods and results: RG was administered, intraperitoneally, for 28 days (2 mg/kg) starting 24 h after MI induction. Echocardiography analysis revealed a significant reduction in left ventricular end-systolic and diastolic dimensions and preserved fractional shortening in RG-treated compared with normal saline group at 28 days post-MI (31.6 ± 2.3 vs. 19.6 ± 1.8, P < 0.0001), respectively. Treatment with RG prevented tissue fibrosis as indicated by interstitial collagen estimation by immunofluorescence staining and hydroxyproline content and attenuated the number of apoptotic myocytes in the border zone (65%) as indicated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) assay. Caspase 3 relative protein levels were significantly decreased in the non-infarcted myocardium. Markedly decreased malondialdehyde levels in the border zone indicate a reduction in tissue oxidative stress.
Conclusions: Our study demonstrates a positive effect of RG in the post-MI period with a significant attenuation in cardiac remodelling.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Cardiac remodelling; Fibrosis; Myocardial infarction; Rasagiline mesylate.
© 2017 The Authors ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


References
-
- Foley PW, Chalil S, Khadjooi K, Irwin N, Smith RE, Leyva F. Left ventricular reverse remodelling, long‐term clinical outcome, and mode of death after cardiac resynchronization therapy. Eur J Heart Fail 2011; 13: 43–51. - PubMed
-
- Tarone G, Balligand JL, Bauersachs J, Clerk A, De Windt L, Heymans S, Hilfiker‐Kleiner D, Hirsch E, Iaccarino G, Knöll R, Leite‐Moreira AF, Lourenço AP, Mayr M, Thum T, Tocchetti CG. Targeting myocardial remodeling to develop novel therapies for heart failure: a position paper from the Working Group on Myocardial Function of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail 2014; 16: 494–508. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Ou L, Liu Y, Liu X, Li F, Sun B, Che Y, Kong D, Yu Y, Steinhoff G. Granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor exacerbates cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction in a rat model of permanent occlusion. Cardiovasc Res 2008; 80: 425–434. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

