Boronic Acid as Glucose-Sensitive Agent Regulates Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment
- PMID: 28772528
- PMCID: PMC5459139
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10020170
Boronic Acid as Glucose-Sensitive Agent Regulates Drug Delivery for Diabetes Treatment
Abstract
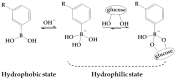
In recent years, glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems have attracted considerable attention in the treatment of diabetes. These systems can regulate payload release by the changes of blood glucose levels continuously and automatically with potential application in self-regulated drug delivery. Boronic acid (BA), especially phenylboronic acid (PBA), as glucose-sensitive agent has been the focus of research in the design of glucose-sensitive platforms. This article reviews the previous attempts at the developments of PBA-based glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems regarding the PBA-functionalized materials and glucose-triggered drug delivery. The obstacles and potential developments of glucose-sensitive drug delivery systems based on PBA for diabetes treatment in the future are also described. The PBA-functionalized platforms that regulate drug delivery induced by glucose are expected to contribute significantly to the design and development of advanced intelligent self-regulated drug delivery systems for treatment of diabetes.
Keywords: diabetes therapy; drug delivery; glucose-sensitivity; phenylboronic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Luo R., Li H. Parameter study of glucose-sensitive hydrogel: Effect of immobilized glucose oxidase on diffusion and deformation. Soft Matter. 2013;11:69–74. doi: 10.1080/1539445X.2011.580412. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

