Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations
- PMID: 28772589
- PMCID: PMC5503371
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10030229
Textural, Structural and Biological Evaluation of Hydroxyapatite Doped with Zinc at Low Concentrations
Abstract
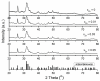
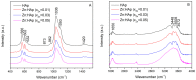
The present work was focused on the synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite doped with low concentrations of zinc (Zn:HAp) (0.01 < xZn < 0.05). The incorporation of low concentrations of Zn2+ ions in the hydroxyapatite (HAp) structure was achieved by co-precipitation method. The physico-chemical properties of the samples were characterized by X-ray Diffraction (XRD), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), zeta-potential, and DLS and N₂-BET measurements. The results obtained by XRD and FTIR studies demonstrated that doping hydroxyapatite with low concentrations of zinc leads to the formation of a hexagonal structure with lattice parameters characteristic to hydroxyapatite. The XRD studies have also shown that the crystallite size and lattice parameters of the unit cell depend on the substitutions of Ca2+ with Zn2+ in the apatitic structure. Moreover, the FTIR analysis revealed that the water content increases with the increase of zinc concentration. Furthermore, the Energy Dispersive X-ray Analysis (EDAX) and XPS analyses showed that the elements Ca, P, O, and Zn were found in all the Zn:HAp samples suggesting that the synthesized materials were zinc doped hydroxyapatite, Ca10-xZnx(PO₄)₆(OH), with 0.01 ≤ xZn ≤ 0.05. Antimicrobial assays on Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli bacterial strains and HepG2 cell viability assay were carried out.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; HepG2 cell viability; Staphylococcus aureus; hydroxyapatite; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Predoi D., Popa C.L., Predoi M.V. Ultrasound studies on magnetic fluids based on maghemite nanoparticles. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2017 doi: 10.1002/pen.24501. - DOI
-
- Glimcher M.J. Bone: Nature of the calcium phosphate crystals and cellular, structural, and physical chemical mechanisms in their formation. In: Sahai N., Schoonen M.A.A., editors. Medical Mineralogy and Geochemistry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry. Volume 64. Mineralogical Society of America; Washington, DC, USA: 2006. pp. 223–282.
-
- Jallot E., Nedelec J.M., Grimault A.S., Chassot E., Grandjean-Laquerriere A., Laquerriere P., Laurent-Maquin D. STEM and EDXS characterisation of physico-chemical reactions at the periphery of sol–gel derived Zn-substituted hydroxyapatites during interactions with biological fluids. Colloid Surf. B. 2005;42:205–210. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2005.03.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

