Investigation on Indentation Cracking-Based Approaches for Residual Stress Evaluation
- PMID: 28772765
- PMCID: PMC5506943
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10040404
Investigation on Indentation Cracking-Based Approaches for Residual Stress Evaluation
Abstract
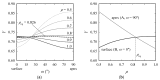
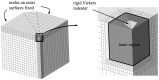
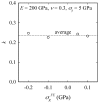
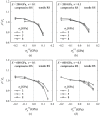
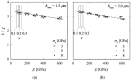
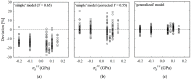
Vickers indentation fracture can be used to estimate equibiaxial residual stresses (RS) in brittle materials. Previous, conceptually-equal, analytical models were established on the assumptions that (i) the crack be of a semi-circular shape and (ii) that the shape not be affected by RS. A generalized analytical model that accounts for the crack shape and its change is presented. To assess these analytical models and to gain detailed insight into the crack evolution, an extended finite element (XFE) model is established. XFE analysis results show that the crack shape is generally not semi-circular and affected by RS and that tensile and compressive RS have different effects on the crack evolution. Parameter studies are performed to calibrate the generalized analytical model. Comparison of the results calculated by the analytical models with XFE results reveals the inaccuracy inherent in the previous analytical models, namely the neglect of (the change of) the crack aspect-ratio, in particular for tensile RS. Previous models should therefore be treated with caution and, if at all, used only for compressive RS. The generalized model, on the other hand, gives a more accurate description of the RS, but requires the crack depth.
Keywords: extended finite element analysis; fracture toughness; indentation fracture; residual stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Warren A.W., Guo Y.B., Weaver M.L. The influence of machining induced residual stress and phase transformation on the measurement of subsurface mechanical behavior using nanoindentation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006;200:3459–3467. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2004.12.028. - DOI
-
- Golovin Y.I. Nanoindentation and mechanical properties of solids in submicrovolumes, thin near-surface layers, and films: A Review. Phys. Solid State. 2008;50:2205–2236. doi: 10.1134/S1063783408120019. - DOI
-
- Groth B.P., Langan S.M., Haber R.A., Mann A.B. Relating residual stresses to machining and finishing in silicon carbide. Ceram. Int. 2016;42:799–807. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.179. - DOI
-
- Wang C., Jiang C., Cai F., Zhao Y., Zhu K., Chai Z. Effect of shot peening on the residual stresses and microstructure of tungsten cemented carbide. Mater. Des. 2016;95:159–164. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.01.101. - DOI
-
- Rossini N.S., Dassisti M., Benyounis K.Y., Olabi A.G. Methods of measuring residual stresses in components. Mater. Des. 2012;35:572–588. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.08.022. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

