Improved Gene Transfer with Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles of Reduced Cytotoxicity
- PMID: 28773087
- PMCID: PMC5551774
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10070731
Improved Gene Transfer with Functionalized Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles of Reduced Cytotoxicity
Abstract
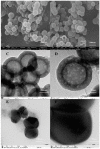
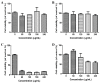
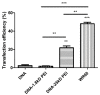
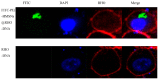
Gene therapy is a promising strategy for treatment of genetically caused diseases. Successful gene delivery requires an efficient carrier to transfer the desired gene into host cells. Recently, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) functionalized with 25 kD polyethyleneimine (PEI) were extensively used as gene delivery carriers. However, 25 kD PEI could significantly reduce the safety of the modified MSNs although it is efficient for intracellular delivery of nucleic acids. In addition, limited drug loading remains a challenge for conventional MSNs drug carriers. Hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles (HMSNs) with high pore volume, tunable pore size, and excellent biocompatibility are attractive alternatives. To make them more efficient, a less toxic 1.8 kD PEI polymer was used to functionalize the HMSNs which have large pore size (~10 nm) and form PEI-HMSNs. Scanning and transmission electron microscopic images showed that HMSNs were spherical in shape and approximately 270 nm in diameter with uniform hollow nanostructures. The maximum loading capacity of green fluorescent protein labeled DNA (GFP-DNA) in PEI-HMSNs was found to be 37.98 mg/g. The loading capacity of PEI-HMSNs was nearly three-fold higher than those of PEI modified solid nanoparticles, indicating that both hollow and large pores contributed to the increase in DNA adsorption. The transfection of GFP-DNA plasmid loaded in PEI-HMSNs was increased two-fold in comparison to that of 25 kD PEI. MTT assays in Lovo cells showed that the cell viability was more than 85% when the concentration of PEI-HMSNs was 120 µg/mL, whereas the cell viability was less than 20% when the 25 kD PEI was used at the same concentration. These results indicated that PEI-HMSNs could be used as a delivery system for nucleic acids due to good biocompatibility, high gene loading capacity, and enhanced gene transfer efficiency.
Keywords: PEI; cytotoxicity; gene transfer; hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our works, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

