In Vivo Damage of the Head-Neck Junction in Hard-on-Hard Total Hip Replacements: Effect of Femoral Head Size, Metal Combination, and 12/14 Taper Design
- PMID: 28773095
- PMCID: PMC5551776
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10070733
In Vivo Damage of the Head-Neck Junction in Hard-on-Hard Total Hip Replacements: Effect of Femoral Head Size, Metal Combination, and 12/14 Taper Design
Abstract
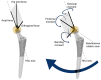
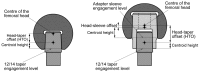
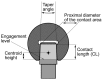
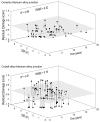
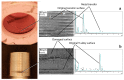
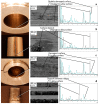
Recently, concerns have been raised about the potential effect of head-neck junction damage products at the local and systemic levels. Factors that may affect this damage process have not been fully established yet. This study investigated the possible correlations among head-neck junction damage level, implant design, material combination, and patient characteristics. Head-neck junctions of 148 retrieved implants were analysed, including both ceramic-on-ceramic (N = 61) and metal-on-metal (N = 87) bearings. In all cases, the male taper was made of titanium alloy. Damage was evaluated using a four-point scoring system based on damage morphology and extension. Patient age at implantation, implantation time, damage risk factor, and serum ion concentration were considered as independent potential predicting variables. The damage risk factor summarises head-neck design characteristics and junction loading condition. Junction damage correlated with both implantation time and damage factor risk when the head was made of ceramic. A poor correlation was found when the head was made of cobalt alloy. The fretting-corrosion phenomenon seemed mainly mechanically regulated, at least when cobalt alloy components were not involved. When a component was made of cobalt alloy, the role of chemical phenomena increased, likely becoming, over implantation time, the damage driving phenomena of highly stressed junctions.
Keywords: fretting corrosion; hard-on-hard bearings; head-neck junction; total hip replacements.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Collier J.P., Surprenant V.A., Jensen R.E., Mayor M.B., Surprenant H.P. Corrosion between the components of modular femoral hip prostheses. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1992;74:511–517. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

