Hydrothermal Sterilization Improves Initial Osteoblast Responses on Sandpaper-Polished Titanium
- PMID: 28773174
- PMCID: PMC5551855
- DOI: 10.3390/ma10070812
Hydrothermal Sterilization Improves Initial Osteoblast Responses on Sandpaper-Polished Titanium
Abstract
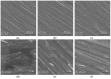
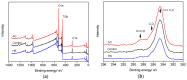
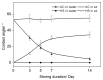
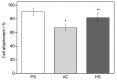
Hydrocarbon contamination accumulated on titanium (Ti) implant surfaces during storage and sterilization is unavoidable and difficult to remove. It impairs the bioactivity of implants, restricts initial interactions between implants and the surrounding biological environment, and has become a common challenge for Ti implants. To overcome this problem, sterilization was considered as the final surface modification and a novel method, hydrothermal sterilization (HS), was proposed. Briefly, stored sandpaper-polished Ti specimens were sterilized in a glass container with pure water at 121 °C for 20 min and kept in the same water until utilization. As a control, another group of specimens was sterilized with conventional autoclaving (AC) at 121 °C for 20 min and stored in sterilization pouches after being dried at 60 °C. Compared with AC, HS deposited numerous nano-sized particles on the substrates, reduced the atomic percentage of the surface carbon, and transformed the Ti surface to a super hydrophilic status. HS also increased the attachment rate, spread, proliferation, and the mineralized nodule areas of rat bone marrow-derived osteoblasts. These results suggest that HS enhances the bioactivity of Ti implants for osteoblasts, and that this biofunctionalization was attributed to nanostructure construction, hydrophilic conversion, and the effective removal of hydrocarbons. Hydrothermal sterilization is proposed to be used as a universal sterilization method for all kinds of titanium implants without apatite coating.
Keywords: hydrothermal; osteoblast; sterilization; surface contamination; titanium implant.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Improved osseointegration of long-term stored SLA implant by hydrothermal sterilization.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016 Jan;53:312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2015.08.038. Epub 2015 Sep 8. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016. PMID: 26382972
-
Influence of sterilization on the performance of anodized nanoporous titanium implants.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021 Nov;130:112429. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2021.112429. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021. PMID: 34702514
-
Exploring the mechanism behind improved osteointegration of phosphorylated titanium implants with hierarchically structured topography.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019 Dec 1;184:110520. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110520. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019. PMID: 31590052
-
A comparative study of the influence of three pure titanium plates with different micro- and nanotopographic surfaces on preosteoblast behaviors.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013 Nov;101(11):3278-84. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34612. Epub 2013 Apr 29. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013. PMID: 23625827
-
Nanostructured titanium surfaces fabricated by hydrothermal method: Influence of alkali conditions on the osteogenic performance of implants.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019 Jan 1;94:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.08.069. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019. PMID: 30423681
Cited by
-
Sterilization protocol for porous dental implants made by Selective Laser Melting.Clujul Med. 2018 Oct;91(4):452-457. doi: 10.15386/cjmed-987. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Clujul Med. 2018. PMID: 30564023 Free PMC article.
-
Sandblasted and Acid Etched Titanium Dental Implant Surfaces Systematic Review and Confocal Microscopy Evaluation.Materials (Basel). 2019 May 30;12(11):1763. doi: 10.3390/ma12111763. Materials (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31151256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surface Modification of Direct-Current and Radio-Frequency Oxygen Plasma Treatments Enhance Cell Biocompatibility.Materials (Basel). 2017 Oct 25;10(11):1223. doi: 10.3390/ma10111223. Materials (Basel). 2017. PMID: 29068417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Branemark P.I., Hansson B.O., Adell R., Breine U., Lindstrom J., Hallen O., Ohman A. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw: Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. 1977;16:1–132. - PubMed
-
- Lum L.B., Beirne O.R., Curtis D.A. Histologic evaluation of hydroxylapatite-coated versus uncoated titanium blade implants in delayed and immediately loaded applications. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1991;6:456–462. - PubMed
-
- Xu L., Shi X., Ouyang C., Liu W. In vitro apatite formation, protein adsorption and initial osteoblast responses on titanium surface enriched with magnesium. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2017;46:1512–1517.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

