Aqueous-Based Coaxial Electrospinning of Genetically Engineered Silk Elastin Core-Shell Nanofibers
- PMID: 28773344
- PMCID: PMC5502692
- DOI: 10.3390/ma9040221
Aqueous-Based Coaxial Electrospinning of Genetically Engineered Silk Elastin Core-Shell Nanofibers
Abstract
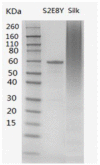
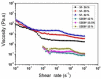
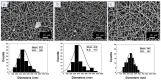
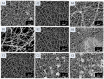
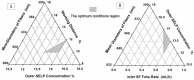
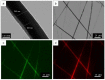
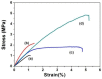
A nanofabrication method for the production of flexible core-shell structured silk elastin nanofibers is presented, based on an all-aqueous coaxial electrospinning process. In this process, silk fibroin (SF) and silk-elastin-like protein polymer (SELP), both in aqueous solution, with high and low viscosity, respectively, were used as the inner (core) and outer (shell) layers of the nanofibers. The electrospinnable SF core solution served as a spinning aid for the nonelectrospinnable SELP shell solution. Uniform nanofibers with average diameter from 301 ± 108 nm to 408 ± 150 nm were obtained through adjusting the processing parameters. The core-shell structures of the nanofibers were confirmed by fluorescence and electron microscopy. In order to modulate the mechanical properties and provide stability in water, the as-spun SF-SELP nanofiber mats were treated with methanol vapor to induce β-sheet physical crosslinks. FTIR confirmed the conversion of the secondary structure from a random coil to β-sheets after the methanol treatment. Tensile tests of SF-SELP core-shell structured nanofibers showed good flexibility with elongation at break of 5.20% ± 0.57%, compared with SF nanofibers with an elongation at break of 1.38% ± 0.22%. The SF-SELP core-shell structured nanofibers should provide useful options to explore in the field of biomaterials due to the improved flexibility of the fibrous mats and the presence of a dynamic SELP layer on the outer surface.
Keywords: coaxial electrospinning; core-shell structure; silk fibroin; silk-elastin-like protein polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. This includes employment, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, grants or patents received or pending or royalties.
Figures


References
-
- Alessandrino A., Marelli B., Arosio C., Fare S., Tanzi M.C., Freddi G. Electrospun silk fibroin mats for tissue engineering. Eng. Life Sci. 2008;8:219–225. doi: 10.1002/elsc.200700067. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

