Specific Ion Effects in Cholesterol Monolayers
- PMID: 28773463
- PMCID: PMC5503052
- DOI: 10.3390/ma9050340
Specific Ion Effects in Cholesterol Monolayers
Abstract
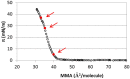
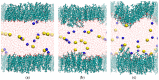
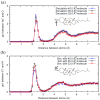
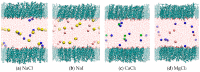
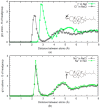
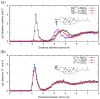
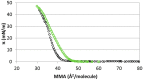
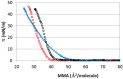
The interaction of ions with interfaces and, in particular, the high specificity of these interactions to the particular ions considered, are central questions in the field of surface forces. Here we study the effect of different salts (NaI, NaCl, CaCl₂ and MgCl₂) on monolayers made of cholesterol molecules, both experimentally (surface area vs. lateral pressure isotherms measured by a Langmuir Film Balance) and theoretically (molecular dynamics (MD) all-atomic simulations). We found that surface isotherms depend, both quantitatively and qualitatively, on the nature of the ions by altering the shape and features of the isotherm. In line with the experiments, MD simulations show clear evidences of specific ionic effects and also provide molecular level details on ion specific interactions with cholesterol. More importantly, MD simulations show that the interaction of a particular ion with the surface depends strongly on its counterion, a feature ignored so far in most theories of specific ionic effects in surface forces.
Keywords: Langmuir monolayers; cholesterol; ionic specificity; molecular dynamics simulations; surface forces.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Evans D.F., Wennerström H. The Colloidal Domain: Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Technology Meet. VCH Publishers; New York, NY, USA: 1999.
-
- Kunz W. Specific ion effects in colloidal and biological systems. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;15:34–39. doi: 10.1016/j.cocis.2009.11.008. - DOI
-
- Marcus Y. Ions in Water and Biophysical Implications: From Chaos to Cosmos. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2012.
-
- Alberts B. Molecular Biology of the Cell. Garland Science; New York, NY, USA: 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

