Using omics approaches to understand pulmonary diseases
- PMID: 28774304
- PMCID: PMC5543452
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-017-0631-9
Using omics approaches to understand pulmonary diseases
Abstract
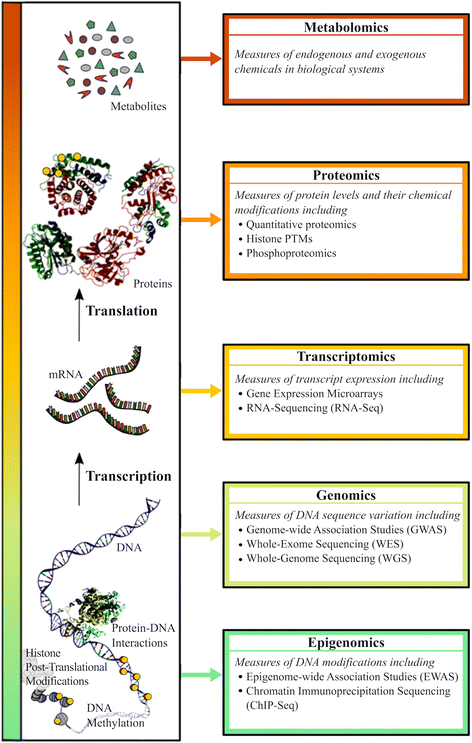
Omics approaches are high-throughput unbiased technologies that provide snapshots of various aspects of biological systems and include: 1) genomics, the measure of DNA variation; 2) transcriptomics, the measure of RNA expression; 3) epigenomics, the measure of DNA alterations not involving sequence variation that influence RNA expression; 4) proteomics, the measure of protein expression or its chemical modifications; and 5) metabolomics, the measure of metabolite levels. Our understanding of pulmonary diseases has increased as a result of applying these omics approaches to characterize patients, uncover mechanisms underlying drug responsiveness, and identify effects of environmental exposures and interventions. As more tissue- and cell-specific omics data is analyzed and integrated for diverse patients under various conditions, there will be increased identification of key mechanisms that underlie pulmonary biological processes, disease endotypes, and novel therapeutics that are efficacious in select individuals. We provide a synopsis of how omics approaches have advanced our understanding of asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), and pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), and we highlight ongoing work that will facilitate pulmonary disease precision medicine.
Keywords: Epigenomics; Genomics; Metabolomics; Proteomics; Pulmonary diseases; Transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials