miR-15a/16 inhibits TGF-beta3/VEGF signaling and increases retinal endothelial cell barrier proteins
- PMID: 28774775
- PMCID: PMC5896299
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.07.007
miR-15a/16 inhibits TGF-beta3/VEGF signaling and increases retinal endothelial cell barrier proteins
Abstract
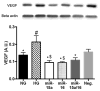
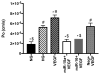
Hyperglycemia is a significant risk factor for diabetic retinopathy and induces multiple biochemical changes, including inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in the retina. Alterations in microRNA expression have been implicated in the pathological responses of diabetic retinopathy and the manipulation of microRNA may provide powerful strategy for therapeutics. Among the predicted targets of miR-15a and -16 are TGF-beta3, SMAD2/3, and VEGF, all of which are known to play a role in vascular endothelial functions. The purpose of this study was to investigate the hypothesis that miR-15a/16 inhibits TGF-beta3/VEGF signaling to maintain retinal endothelial cell barrier protein levels. Human primary retinal endothelial cells (REC) were maintained in normal (5mM) glucose or transferred to high glucose medium (25mM) for 3days. REC were transfected with miRNA mimics (hsa-miR-15a-5p and -16-5p). Retinal lysates from miR-15a-transgenic mice were also analyzed. We demonstrated that overexpression of miR-15a/16 resulted in decreased TGF-beta3 signaling and VEGF levels in cultured REC grown in high glucose conditions. In addition, the levels of tight junction proteins, zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and occludin, were elevated in REC following overexpression of miR-15a and -16. Overexpression of miR-15a and -16 played a role in reducing cellular permeability through inhibition of VEGF signaling in REC cultured under high glucose conditions. Using miR-15a-transgenic mice, we demonstrated the regulatory role of miR-15a on TGF-beta3 signaling and tight junction proteins in vivo. Our outcomes suggest that miR-15a/16 maintain the retinal endothelial cell barrier by reducing TGFbeta3/VEGF signaling and increasing levels of key tight junction proteins.
Keywords: Retinal endothelial permeability; SMAD2/3; TGF-beta3; VEGF; miR-15a/16.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
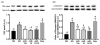
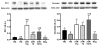
Similar articles
-
miR-146a suppresses STAT3/VEGF pathways and reduces apoptosis through IL-6 signaling in primary human retinal microvascular endothelial cells in high glucose conditions.Vision Res. 2017 Oct;139:15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.03.009. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Vision Res. 2017. PMID: 28433754 Free PMC article.
-
miR-15a/16 reduces retinal leukostasis through decreased pro-inflammatory signaling.J Neuroinflammation. 2016 Dec 8;13(1):305. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0771-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2016. PMID: 27931222 Free PMC article.
-
Compound 49b Regulates ZO-1 and Occludin Levels in Human Retinal Endothelial Cells and in Mouse Retinal Vasculature.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017 Jan 1;58(1):185-189. doi: 10.1167/iovs.16-20412. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28114578 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA Regulation of Endothelial Junction Proteins and Clinical Consequence.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5078627. doi: 10.1155/2016/5078627. Epub 2016 Nov 24. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27999452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cell biology of intraocular vascular diseases].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1999 Dec;103(12):923-47. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1999. PMID: 10643294 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Role of MicroRNA in linking diabetic retinal neurodegeneration and vascular degeneration.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 4;15:1412138. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1412138. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39027475 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA15a regulates insulin signal transduction in the retinal vasculature.Cell Signal. 2018 Apr;44:28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.01.016. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 29339083 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA‑15a‑5p induces pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell apoptosis in a pulmonary arterial hypertension model via the VEGF/p38/MMP‑2 signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Feb;45(2):461-474. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4434. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31894295 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq Revealed Novel Non-proliferative Retinopathy Specific Circulating MiRNAs in T2DM Patients.Front Genet. 2019 Jun 4;10:531. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00531. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31275351 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer Loss in Müller Glia Leads to a Defined Sequence of Pathological Events Beginning With Cone Dysfunction.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025 Mar 3;66(3):7. doi: 10.1167/iovs.66.3.7. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2025. PMID: 40035725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonetti DA, Barber AJ, Khin S, Lieth E, Tarbell JM, Gardner TW, et al. Vascular permeability in experimental diabetes is associated with reduced endothelial occludin content – Vascular endothelial growth factor decreases occludin in retinal endothelial cells. Diabetes. 1998;47:1953–1959. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA, Wolpert EB. Isolation and characterization of retinal endothelial cells. Methods in Molecular Medicine. 2003;89:365–374. - PubMed
-
- Barrios-Rodiles M, Brown KR, Ozdamar B, Bose R, Liu Z, Donovan RS, et al. High-throughput mapping of a dynamic signaling network in mammalian cells. Science. 2005;307:1621–1625. - PubMed
-
- Behzadian MA, Wang XL, Windsor LJ, Ghaly N, Caldwell RB. TGF-beta increases retinal endothelial cell permeability by increasing MMP-9: Possible role of glial cells in endothelial barrier function. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 2001;42:853–859. - PubMed
-
- Behzadian MA, Windsor LJ, Ghaly N, Liou G, Tsai NT, Caldwell RB. VEGF-induced paracellular permeability in cultured endothelial cells involves urokinase and its receptor. FASEB Journal. 2003;17:752–754. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

