Epidemiology and Natural History of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- PMID: 28774845
- PMCID: PMC5794619
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.067
Epidemiology and Natural History of Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Abstract
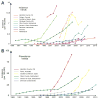
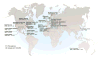
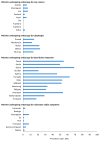
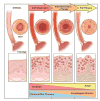
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) has emerged over the past 2 decades as a major cause of upper gastrointestinal morbidity. Over this time, the epidemiology of EoE has also rapidly evolved. EoE has transformed from a rare case-reportable condition to disease that is commonly encountered in the gastroenterology clinic, hospital emergency room, and endoscopy suite. The incidence and prevalence are increasing at rates that outpace increased disease recognition. Current incidence estimates range from 5 to 10 cases per 100,000, and current prevalence estimates range from 0.5 to 1 case per 1000. We review the data and potential reasons behind this increase, examine risk factors, and identify important areas for research into disease etiology. The article also discusses the progression of EoE from an inflammatory to fibrostenotic phenotype. An accurate view of the natural history of EoE is central to discussions with patients regarding disease prognosis and decisions about long-term use of medical, endoscopic, and diet therapies. Progressive remodelling appears to be gradual, but not universal, and the duration of untreated disease is the best predictor of stricture risk. Ultimately, prospective, long-term outcome studies focusing on multiple aspects of disease activity are needed to fully understand the natural history of EoE.
Keywords: Fibrosis; Incidence; Prevalence; Progression.
Copyright © 2018 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, Attwood SE, Bonis PA, Burks AW, Chehade M, Collins MH, Dellon ES, Dohil R, Falk GW, Gonsalves N, Gupta SK, Katzka DA, Lucendo AJ, Markowitz JE, Noel RJ, Odze RD, Putnam PE, Richter JE, Romero Y, Ruchelli E, Sampson HA, Schoepfer A, Shaheen NJ, Sicherer SH, Spechler S, Spergel JM, Straumann A, Wershil BK, Rothenberg ME, Aceves SS. Eosinophilic esophagitis: Updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20. e6. - PubMed
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, Liacouras C, Katzka DA. ACG Clinical Guideline: Evidence based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–92. - PubMed
-
- Dobbins JW, Sheahan DG, Behar J. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with esophageal involvement. Gastroenterology. 1977;72:1312–6. - PubMed
-
- Landres RT, Kuster GG, Strum WB. Eosinophilic esophagitis in a patient with vigorous achalasia. Gastroenterology. 1978;74:1298–1301. - PubMed
-
- Attwood SE, Smyrk TC, Demeester TR, Jones JB. Esophageal eosinophilia with dysphagia. A distinct clinicopathologic syndrome. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:109–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

