Role of G protein-coupled receptors-microRNA interactions in gastrointestinal pathophysiology
- PMID: 28774868
- PMCID: PMC5792214
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00144.2017
Role of G protein-coupled receptors-microRNA interactions in gastrointestinal pathophysiology
Abstract
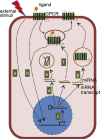
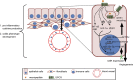
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) make up the largest transmembrane receptor superfamily in the human genome and are expressed in nearly all gastrointestinal cell types. Coupling of GPCRs and their respective ligands activates various phosphotransferases in the cytoplasm, and, thus, activation of GPCR signaling in intestine regulates many cellular and physiological processes. Studies in microRNAs (miRNAs) demonstrate that they represent critical epigenetic regulators of different pathophysiological responses in different organs and cell types in humans and animals. Here, we reviewed recent research on GPCR-miRNA interactions related to gastrointestinal pathophysiology, such as inflammatory bowel diseases, irritable bowel syndrome, and gastrointestinal cancers. Given that the presence of different types of cells in the gastrointestinal tract suggests the importance of cell-cell interactions in maintaining gastrointestinal homeostasis, we also discuss how GPCR-miRNA interactions regulate gene expression at the cellular level and subsequently modulate gastrointestinal pathophysiology through molecular regulatory circuits and cell-cell interactions. These studies helped identify novel molecular pathways leading to the discovery of potential biomarkers for gastrointestinal diseases.
Keywords: epigenetics; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; intestinal epithelial cells; microribonucleic acid; neuropeptides.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of microRNAs in gastrointestinal smooth muscle fibrosis and dysfunction: novel molecular perspectives on the pathophysiology and therapeutic targeting.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Apr 1;310(7):G449-59. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00445.2015. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26822916 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Onco-GPCR signaling and dysregulated expression of microRNAs in human cancer.J Hum Genet. 2017 Jan;62(1):87-96. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2016.124. Epub 2016 Oct 13. J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 27734836 Review.
-
Significance of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor in the Pathophysiology of Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colorectal Cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 Jun 12;11:390. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00390. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32595606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms of ligand binding, signaling, and regulation within the superfamily of G-protein-coupled receptors: molecular modeling and mutagenesis approaches to receptor structure and function.Pharmacol Ther. 2004 Jul;103(1):21-80. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2004.05.002. Pharmacol Ther. 2004. PMID: 15251227 Review.
-
Expression and Function of miR-155 in Diseases of the Gastrointestinal Tract.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 11;17(5):709. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050709. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27187359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knockdown of miR-19a suppresses gastrointestinal dysmotility diarrhea after TBI by regulating VIP expression.Brain Behav. 2023 Jul;13(7):e3071. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3071. Epub 2023 May 22. Brain Behav. 2023. PMID: 37218372 Free PMC article.
-
GPCRomics: An Approach to Discover GPCR Drug Targets.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Jun;40(6):378-387. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2019.04.001. Epub 2019 May 8. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31078319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into neurokinin 3 receptor activation by endogenous and analogue peptide agonists.Cell Discov. 2023 Jun 30;9(1):66. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00564-w. Cell Discov. 2023. PMID: 37391393 Free PMC article.
-
Role of microRNAs in Disorders of Gut-Brain Interactions: Clinical Insights and Therapeutic Alternatives.J Pers Med. 2021 Oct 12;11(10):1021. doi: 10.3390/jpm11101021. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 34683162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alexander SPH, Davenport AP, Kelly E, Marrion N, Peters JA, Benson HE, Faccenda E, Pawson AJ, Sharman JL, Southan C, Davies JA, Collaborators C; CGTP Collaborators . The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2015/16: G protein-coupled receptors. Br J Pharmacol 172: 5744–5869, 2015. doi:10.1111/bph.13348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakirtzi K, Hatziapostolou M, Karagiannides I, Polytarchou C, Jaeger S, Iliopoulos D, Pothoulakis C. Neurotensin signaling activates microRNAs-21 and −155 and Akt, promotes tumor growth in mice, and is increased in human colon tumors. Gastroenterology 141: 1749–1761, 2011. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bao W, Fu HJ, Xie QS, Wang L, Zhang R, Guo ZY, Zhao J, Meng YL, Ren XL, Wang T, Li Q, Jin BQ, Yao LB, Wang RA, Fan DM, Chen SY, Jia LT, Yang AG. HER2 interacts with CD44 to up-regulate CXCR4 via epigenetic silencing of microRNA-139 in gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology 141: 2076–2087, 2011. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.08.050. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

