Enteric serotonin and oxytocin: endogenous regulation of severity in a murine model of necrotizing enterocolitis
- PMID: 28774871
- PMCID: PMC5792212
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00215.2017
Enteric serotonin and oxytocin: endogenous regulation of severity in a murine model of necrotizing enterocolitis
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018 Mar 1;314(3):G459. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.zh3-7428-corr.2018. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29516747 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
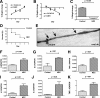
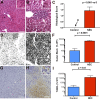
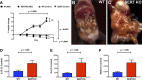
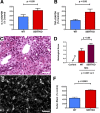
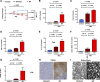
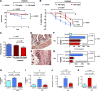
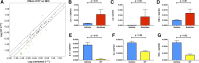
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a gastrointestinal inflammatory disease of unknown etiology that may also affect the liver, causes a great deal of morbidity and mortality in premature infants. We tested the hypothesis that signaling molecules, which are endogenous to the bowel, regulate the severity of intestinal and hepatic damage in an established murine NEC model. Specifically, we postulated that mucosal serotonin (5-HT), which is proinflammatory, would exacerbate experimental NEC and that oxytocin (OT), which is present in enteric neurons and is anti-inflammatory, would oppose it. Genetic deletion of the 5-HT transporter (SERT), which increases and prolongs effects of 5-HT, was found to increase the severity of systemic manifestations, intestinal inflammation, and associated hepatotoxicity of experimental NEC. In contrast, genetic deletion of tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (TPH1), which is responsible for 5-HT biosynthesis in enterochromaffin (EC) cells of the intestinal mucosa, and TPH inhibition with LP-920540 both decrease the severity of experimental NEC in the small intestine and liver. These observations suggest that 5-HT from EC cells helps to drive the inflammatory damage to the gut and liver that occurs in the murine NEC model. Administration of OT decreased, while the OT receptor antagonist atosiban exacerbated, the intestinal inflammation of experimental NEC. Data from the current investigation are consistent with the tested hypotheses-that the enteric signaling molecules, 5-HT (positively) and OT (negatively) regulate severity of inflammation in a mouse model of NEC. Moreover, we suggest that mucosally restricted inhibition of 5-HT biosynthesis and/or administration of OT may be useful in the treatment of NEC.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Serotonin (5-HT) and oxytocin reciprocally regulate the severity of intestinal inflammation and hepatotoxicity in a murine model of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). Selective depletion of mucosal 5-HT through genetic deletion or inhibition of tryptophan hydroxylase-1 ameliorates, while deletion of the 5-HT uptake transporter, which increases 5-HT availability, exacerbates the severity of NEC. In contrast, oxytocin reduces, while the oxytocin receptor antagonist atosiban enhances, NEC severity. Peripheral tryptophan hydroxylase inhibition may be useful in treatment of NEC.
Keywords: inflammation; intestine; necrotizing enterocolitis; oxytocin; serotonin.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
References
-
- Afrazi A, Branca MF, Sodhi CP, Good M, Yamaguchi Y, Egan CE, Lu P, Jia H, Shaffiey S, Lin J, Ma C, Vincent G, Prindle T Jr, Weyandt S, Neal MD, Ozolek JA, Wiersch J, Tschurtschenthaler M, Shiota C, Gittes GK, Billiar TR, Mollen K, Kaser A, Blumberg R, Hackam DJ. Toll-like receptor 4-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal crypts induces necrotizing enterocolitis. J Biol Chem 289: 9584–9599, 2014. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.526517. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bischoff SC, Mailer R, Pabst O, Weier G, Sedlik W, Li Z, Chen JJ, Murphy DL, Gershon MD. Role of serotonin in intestinal inflammation: knockout of serotonin reuptake transporter exacerbates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid colitis in mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 296: G685–G695, 2009. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90685.2008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Blakely RD, De Felice LJ, Hartzell HC. Molecular physiology of norepinephrine and serotonin transporters. J Exp Biol 196: 263–281, 1994. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

